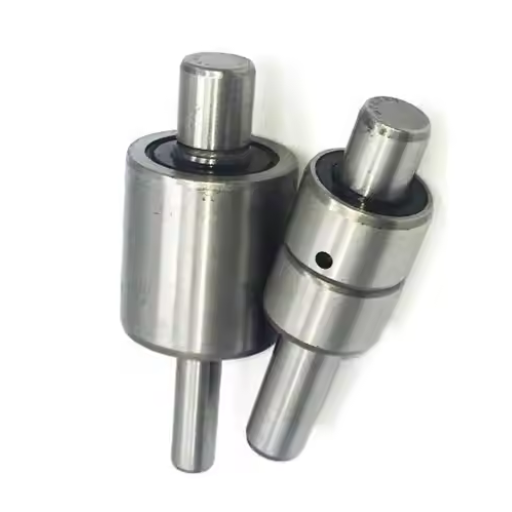
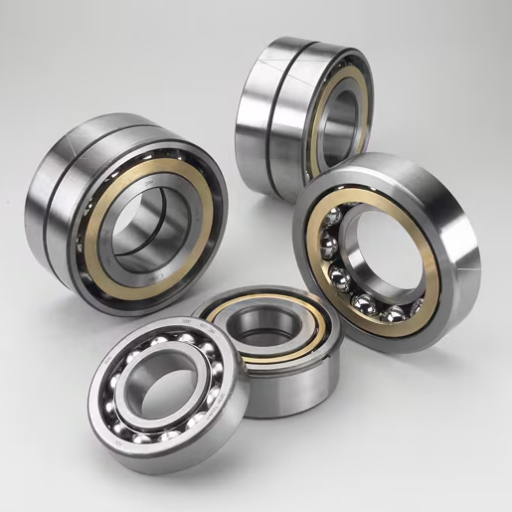
The water pump bearings, which are auto shafts, are vital for the operations of modern automotive water cooling systems. These bearings allow smooth and efficient performance by supporting the shaft of the water pump which helps in the engine’s coolant distribution. Quality bearings minimize the friction and wear of the water pump, making it last longer while ensuring that the engine operates efficiently under different settings. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the importance of these bearings, how they affect the dependability of a vehicle, and the most important reasons why investing in the best quality options that can avoid expensive repairs and improve overall automotive efficiency is worth investing.
How Does a Water Pump Work in an Automotive Engine?
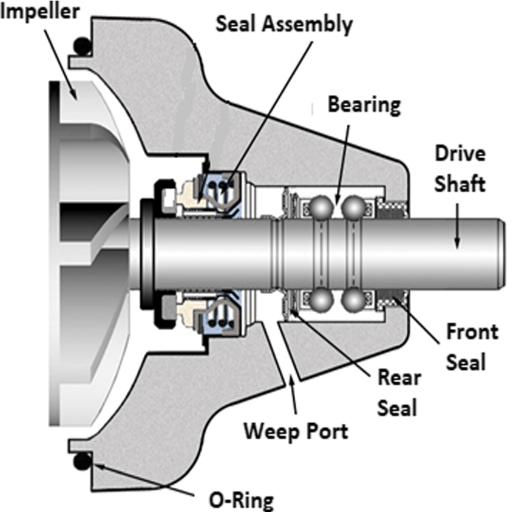
What Role Does the Shaft Play in the Water Pump?
The shaft is an important part of the water pump because it most directly affects its performance. The shaft transfers coolant from the impeller to the drive mechanism, facilitating the water pump’s rotation. It also enables the water pump to rotate so that it can circulate the coolant around the engine. A shaft can be considered optimal if it can withstand high torque and rotational speeds while remaining in alignment and being durable under different working conditions.
From a technical perspective, the operation or performance of a shaft affects and influences the following:
Torque Capacity—To perform some degree of rotation, a shaft should be able to brace against the torque produced by an engine as long as it does not snap or warp. This ensures proper operation and no straying alignment.
Rotational Speed—At a certain point, the shaft’s working rpm increases, and due to the risk of vibration and wear, the shaft needs a higher quality specification, which would reduce the pump’s effectiveness.
Material Strength and Corrosion Resistance—Due to its durability, an alloy-treated metal is the preferred worn, fatigued, and coolant-exposed material.
Bearing Compatibility – Since the shaft works together with the bearings, its balance has to use less energy to overcome any friction, which contributes to a prolonged water pump.
Having optimized these parameters, the shaft directly impacts the reliability and effectiveness of water pump performance, which positively impacts an engine’s cooling and safe functioning.
What Components Are Essential for Efficient Water Pump Operation?
The main points I take into account when analyzing the parameters of the water pump system and its components are:
Impeller – Coolant circulating through the system is achieved using an impeller. The construction efficiency of the impeller is determined by its blade angles and the material it is made of. These two factors permit the system to operate effectively without too much cavitation.
Mechanical Seal—The seal prevents coolant leaks from the system while the water pump operates at different pressures and temperatures. A seal made of high-quality material allows the system to maintain structural integrity and improves its durability, which in turn aids in pressure retention and enhances the system’s general performance.
Bearings—Bearings permit the shaft to rotate. Many factors, such as capacity to withstand load and resistance to wear, need to be considered when selecting the bearings for the water pump. Opting for the wrong bearings increases friction on the water pump, diminishing its productive service life.
Shaft—This connects the drive mechanism to the impeller. A durable balance shaft produces fewer vibrations and less wear components and generally provides smoother operating conditions.
Housing serves as a protective barrier for internal components and structural support for the unit. The ability to withstand coolant and thermal expansion is essential for any coolant system, and housing reliability determines a significant portion of system dependability.
All the elements mentioned impact several technical aspects, including the coolant flow rate, pressure stability, wear resistance, and thermal tolerance. By optimizing and preserving these constituents, I can ensure the smooth operation of the water pumps.
How to Do Ball Bearings and Roller Bearings Function?
Both ball bearings and roller bearings serve two distinctive purposes for facilitating motion in linear or rotary parts by reducing friction between the moving parts. To be more specific, high-speed applications where low friction is crucial employ ball bearings that have spherical balls to take care of both radial and axial loads. Compared to ball bearings, roller bearings have lower speeds but can withstand greater radial loads thanks to cylindrical rolling elements.
In my opinion, the selection of these bearings influences the critical water pump design parameters. For example:
Load Capacity: Roller bearings can take high radial loads, making them useful in applications with high mechanical stress.
Friction Reduction: Due to their design, ball bearings are better at reducing friction, allowing for smoother functioning and energy conservation.
Wear Resistance: Although both types challenge the problem of wear over time, their effectiveness depends on the load types and the pump’s operational speeds.
Durability at Speed: Compared to other types, ball bearings are the most suited for high speeds since they resist overheating while remaining stable and efficient.
Working within these parameters would allow me to select the appropriate bearing type for the pump’s design, which would optimize its performance while extending its service life and maintaining operational standards.
Why Is Bearing Quality Crucial in Water Pump Systems?

What Are the Risks of Bearing Failure in a Water Pump?
Risks of Functional Efficiency & Overall Effectiveness—Water Pump Bearing Failure Cost Analysis If a bearing in a system-integrated water pump fails or gets damaged, it jeopardizes varying degrees of risks that hinder efficient functionality. Water Pumps are made to rotate, and when pumping system bearings fail, overheating rises due to excessive friction, energy consumption, and reduced operational efficiency. In such cases, the potential for damage to the water heating system components also grows significantly.
Considered from critical practical dimensional analysis, the most pertinent factors for determining the magnitude of the consequences as mentioned earlier are as follows;
Rotational Speed—Bearing issues practically disable the pump’s capacity to sustain the set rotational speeds, leading to drastic drops in performance and heightened vibration.
Axial and Radial Load Capacity – A failed bearing cannot adequately support highly eccentric and combined loading, leading to shaft destruction or alignment problems.
Temperature Thresholds – Excessive frictional losses in the bearings cause the system operating temperature to exceed any degree that can be controlled, risking a total breakdown.
Lubrication efficiency – Inaccurate bearing constructions result in flooded conditions and further drift towards shaft drops beyond acceptable parameters, leading to worn-down ends and discomforting the ease of movement for the decrease in the life of the pump unit.
To eliminate such risks, it becomes expedient to perform regular inspections of bearing conditions, control operational parameters, and use high-quality bearings compliant with the requirements of the water pump system.
How Do Bearings Provide Durability and Longevity?
Bearings significantly focus on water pump systems as they enhance their operation and increase durability due to reduced friction and wear. The selection of the correct bearings is crucial as the high-quality ones ensure proper load distribution, reducing stress and preventing premature failure. Some of the factors that affect the selection are:
Load Capacity: Bearings must cater to radial and axial loads without the risk of deformation or damage for assured performance.
Rotational Speed: To avoid overheating the system, the proper bearing design must ensure that efficiency is maintained at high speeds with reduced heat generation.
Material Quality: High-grade materials’ ability to withstand fatigue and corrosion adds to their durability, which is essential, especially in harsh environments.
Moreover, the ability to withstand the wear and tear of the system is also crucial.
Alignment Precision: Normal internal stresses caused by vibration on the water pump system allow for correct alignment, which helps reduce the loss of system integrity.
These parameters, along with systematic and regular maintenance, enable smoother system operation while enhancing the bearings’ overall life and reliability.
How Can Lubrication Affect Bearing Performance?
Lubricants have a huge impact on the performance of bearings by decreasing the levels of friction, wear, and heat created in the process, which, from my experience, increases the operational efficiency and the lifetime of the bearings. Proper lubrication has ratios of impact that define it as optimal, I detail them below:
Friction Reduction—Proper lubrication reduces contact between metals, which results in lower resistance to moving parts. Therefore, energy is utilized more efficiently.
Temperature Control—Lubrication controls heat by reducing the friction that builds up between moving parts. If heat is allowed to build up, surrounding materials tend to degrade, and the lifetime of the bearings suffers greatly.
Load Distribution—A lubricated bearing adequately allows rolling elements to distribute stress evenly, minimizing directly applied stress and distortion of the elements.
Corrosion Protection – Protecting bearing surfaces from moisture and pollutants with high-grade lubricants will prevent corrosion, which destroys surrounding materials.
Vibration Dampening – Well lubricated bodies reduces the effect of small shocks and vibrations, therefore loosening of surrounding parts is avoided which creates ill-functioning systems.
When targeted lubricants are applied under the recommended intervals, it allows me to achieve optimal performance of the bearings while attending to the specific technical needs of the system without a problem.
What Are the Different Types of Water Pump Bearings?
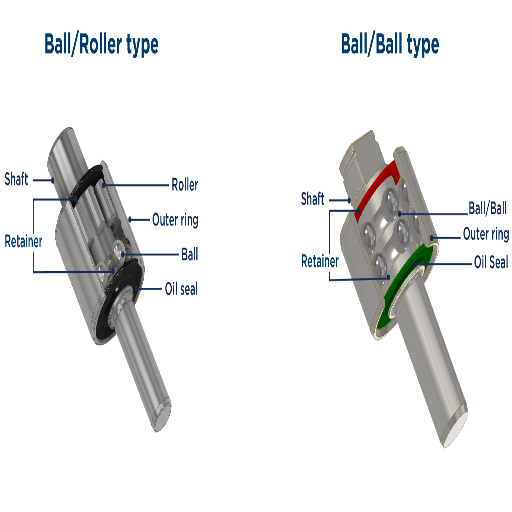
How Do Ball Bearings Differ from Roller Bearings?
There are notable differences between ball bearings and roller bearings regarding structure, function, and usage.
1. Structural Differences:
Spherical balls are used in ball bearings as rolling elements. These balls provide rotating points of contact at the raceways, reducing friction and ensuring smooth rotation.
Roller Bearings are noted for using cylindrical, tapered, or needle-shaped rollers as rolling elements. These rollers provide line contact with the raceways, which increases their capacity to carry the load.
2. Load Capacity:
Ball Bearings are made to accommodate radial (lying perpendicular to the axis) and axial (paralleled to the axis) loads, which they can sustain better than other apparatuses, but only if they are light in weight.
Roller Bearings manage high radial loads better due to their more extensive contact area. Tapered roller bearings are also excellent for axial loads.
3. Applications:
Due to their low friction and smooth motion, Ball Bearings are ideal for high-speed and low-load functions like electric motors, fans, and micro-machines.
Roller Bearings work best with higher loads at low speeds and are common in conveyor belts, gearboxes, industrial machinery, and many more.
When selecting between ball bearings and roller bearings, the operational requirements, such as smoothness of motion, type of load, and the surrounding environment, need to be carefully examined for thorough effectiveness.
What Is a Cylindrical Roller Bearing?
A Cylindrical Roller Bearing is a type of bearing designed for high radial load capabilities while ensuring precision and high performance. These bearings possess cylindrical rollers which interface with the raceways linearly. This creates a better provision for friction and torque load distribution. Therefore, these bearings are ideal for applications with moving parts that rotate at high speeds and have heavy radial loads.
Load Capacity: Conversely, these bearings have high efficiency, but the radial load capacity is maximized. Their ability to bear axial loads is somewhat limited considering the design of the bearing, for instance, the single-row versus double-row designs.
Speed Rating: These bearings permit high operational speeds because of low drag friction and fine-tuned manufacturing tolerances.
Material: They are made of bearing-grade steel or high-strength alloys to withstand constant wearing or difficult working conditions.
Temperature Range: The operating temperature range typically ranges between -20° C to 150° C, depending on the lubrication and materials used.
Alignment Tolerance: They generally need precise bearing orientation for good operational performance, as there is low tolerance for misalignment.
Cylindrical roller bearings are primarily designed for electric motor bearings, gearbox bearings, turbine bearings, and many other areas of machinery that require high stability and high speed with considerable load.
Understanding the Spherical and Integral Shaft Bearings
Spherical bearings are suitable for heavy radial and moderate axial loads and are self-aligned, ensuring the bearings operate efficiently between a temperature range of -30 °C to 200 °C, depending on the lubricant used. Their specific design permits angular misalignment between the shaft and housing, which makes these bearings ideal for conditions where alignment can change over time or with heavy load. However, these bearings are not considered suitable for highly high-speed applications.
Conversely, water pumps and other compact machinery can use integral shaft bearings designed with compactness and high durability in mind. These bearings have a pre-lubricated design, meaning less maintenance is required, however, proper sealing is crucial to prevent contamination and increase service life. The operating temperature for these bearings is between -20 °C and 170 °C. With their ability to support combined radial and axial loads while providing high rotational precision, these bearings are undoubtedly suitable for automotive water pumps.
With each type of bearing differing in its technical parameters like load capacity, speed tolerances, and temperature restrictions, it is no surprise that each type has unique advantages depending on the application’s specific requirements.
How to Prevent Bearing Failure in Automotive Water Pumps?
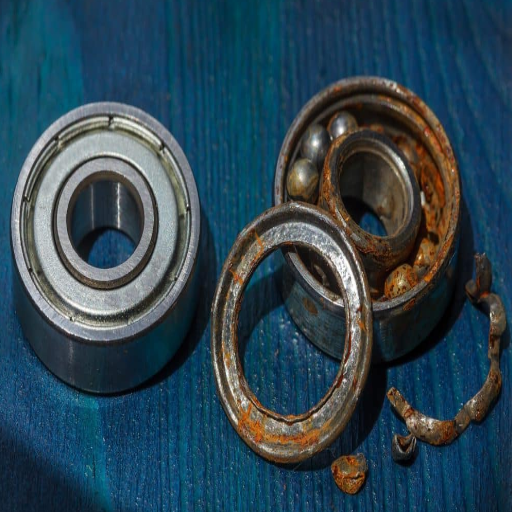

What Maintenance Practices Extend Service Life?
When it comes to increasing the service life of bearings in automotive water pumps, maintenance is one of the key contributing factors. For instance, checking seals is important as effective seals prevent contamination from dirt, debris, and moisture, which can lead to failure and excessive wear. Furthermore, bearings and other engine components also need pre-lubrication, and applying compatible grease is essential. Over-lubrication, however, should be avoided as this can increase temperature and lead to seal damage. In addition to this, vibration levels should also be monitored. Unusual high levels of vibrations can indicate imbalance or misalignment, which can lower precision in rotation.
These approaches reverberate through the technical parameters. In other words, clean and lubricated bearings, along with correct assembly, positively impact the load capacity by reducing friction and wear. Sufficient sealing helps eliminate heat build-up and thus extends the temperature tolerance range. Lastly, all activities to correct the misalignment help preserve speed limits by straining as little as possible on the mechanism of rotation. All steps aid in increasing reliability and the service life of the bearings.
How to Identify Early Signs of Bearing Wear and Tear?
To identify early signs of bearing wear and tear, it is necessary to keep track of several factors in a particular manner:
Strange Noises: Sounds like grinding or clicking and squealing at abnormal frequencies could suggest that internal damage or lubrication is inadequate.
Overheating: Bearings might run hotter than ordinary because they lack lubrication, which often accompanies contamination and internal friction.
Variations in Vibrations: Increased or decreased breaths in vibration may indicate looseness, misalignment, imbalance, or even rolling element wear.
Lubricant Inspection: Check for contamination, discoloration, and breakdown, as poor lubrication always leads to increased wear.
Damage That is Visible: During routine maintenance, look for pitting, spalling, or other deformation of bearing surfaces, which is often visible.
Suppose these factors are monitored continuously along with the technical parameters set by the machines. In that case, one can notice the early symptoms of bearing damage, which can help eradicate the damage and improve efficiency.
What Role Does Proper Installation Play in Bearing Longevity?
The proper implementation of installation procedures significantly affects the relative longevity of bearings as their condition directly affects one’s performance index as well as the expected operational lifespan. Bearing misalignment, excessive preload, and unequal load distribution stemming from improper installation accelerates wear and tear and leads to operational failure. Below are critical technical parameters that require consideration during the installation phase to ensure the maximized functionality of the bearings:
Alignment: Shafts and housings should be appropriately aligned to avoid uneven stress-bearing distribution. Misalignment should not go beyond the specified manufacturer tolerances.
Mounting Force: Standard practice involves applying force to either the inner or outer ring of the bearing. Excessive force, such as hammering and using cloth rags or other unorthodox tools, is not condoned.
Preload & Clearance: Every application demands appropriate preload or clearance, aiming to avoid overheating or operational inefficiencies caused by excessive preload.
Cleanliness: To eliminate contaminants that scratch or corrode the bearings over time, a clean installation environment must be maintained.
Lubrication: Proper application of lubrication guarantees the reduction of operational friction and ensures one’s bearings are not overworked.
The service life of the bearings is bound to improve drastically by following these steps, hence, reducing the chances of undesirable operational downtimes and expensive repair works.
How to Repair or Replace the Water Pump Bearing?
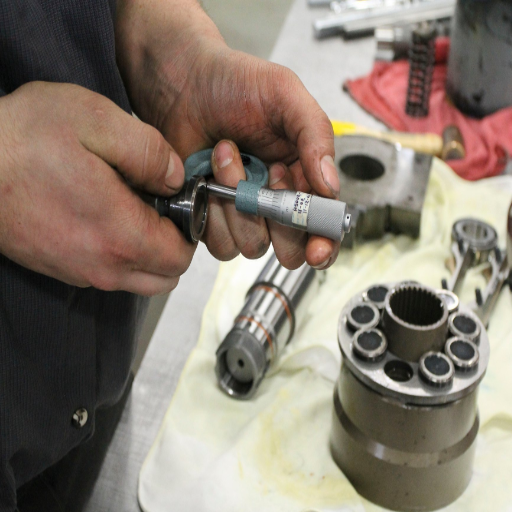

What Are the Steps to Replace the Water Pump?
I would accomplish the practical and technically oriented replacement of the water pump using these steps:
Prepare the Workspace: Prior to everything, make sure to switch off the engine and allow it to cool down completely. Disconnecting the battery is crucial for avoiding any electric harm. The workspace should be clean and well-lit so no contaminants are introduced during reassembly.
Drain the Coolant: Pour the coolant with utmost care to ensure that spillage is minimal while placing the coolant into a designated container. Make sure to dispose of the coolant appropriately; if that is not an option, prepare coolant for refilling.
Remove Associated Components: Remove the drive belt and any timing belt or hoses obstructing the water pump. Take usual precautions and mark and tag expensive parts to ensure correct order during reassembly. Damage to bearings can occur due to improper belt tensioning when reinstalling.
Inspect and Note Technical Parameters: Prior to any removal, thoroughly examine the existing water pump and bolt torque details. Those details will aid in the perfect fitment of the new unit. Contacting the manufacturer for precise instructions is a good idea, as the standard torque variety for the bolts is different for every water pump.
Water Pump Removal: Simply unscrew and remove the pump, but be careful not to use excessive force, as that may damage the surrounding components. Check the surfaces for corrosion and debris; if there is any, scrub it clean.
Water Pump Installation: Gently fix the pump to the mounting surface using the recommended torque to ensure that it does not get damaged while being overtightened. Use a cross-pattern while repeating this process on each bolt to properly balance out the pressure and avoid cracking the housing. Lastly, make sure to check for leaks, which indicate that the water pump was not tight enough.
Coolant Refill: Put back all previously taken-off components, ensuring they are positioned in the correct order. Refill the coolant; before doing so make sure the requirements for the system are met. If any air pockets are left, bleed the system to eliminate them.
System Testing: Connect the battery again and test the engine. Look for any unusual sounds or leaks. Ensure the water pump is set at its technical limits, which include the flow rate and pressure. After the engine has been driven for a few meters, keep track of the coolant level.
All technical values that have been affected due to the changes in the water pump include torque settings, alignment, belt tension, gasket state, and coolant type. If all these parameters are correctly followed, the system can perform excellently.
When Should You Consider a Repair Over Replacement?
In my personal experience, an attempt at a repair is undoubtedly justified when the defect is minor and only relates to some parts, such as a damaged gasket or a loose belt, rather than the whole water pump. The problem, in most cases, can be dealt with by simply repairing a few components without the need to attend to a complete water pump repair. If the water pump is to be serviced, I believe the repair is justified only if the water pump housing is in good shape and there are no other visible advanced signs of wear or corrosion on the system.
Nonetheless, it is important to understand how these repair actions affect some key technical parameters. Take, for instance:
Torque Specifications—Tightening bolts to the specified torque with gaskets may result in leak-free and well-supported housing.
Alignment – Components not set properly can cause overwear to the belt or the pulleys. Proper alignment also helps ensure system efficiency.
Belt Tension – A belt that is not put at the proper tension may cause overworking of the pump. The result is a loss of working efficiency and may worsen the state of the pump.
Gasket Integrity – Not caulking the gasket properly may lead to coolant leaks and loss of operational power.
Coolant Type – After minor repairs, the proper coolant should be used as top-offs to make sure that there is no harm caused by inappropriate fluids.
Deciding on a repair can save time and finances while retaining functionality, as long as each technical aspect is considered for optimum outcomes.
What Tools Are Necessary for Water Pump Bearing Repair?
In my opinion, the following tools would be necessary for adequate repair of a water pump bearing:
Socket Set and Wrenches—These tools are imperative for loosening and tightening bolts with the correct torque application to prevent leaks or damage to the housing wall.
Pulley Puller Tool: This tool helps to remove the pulley without damaging structural components, ensuring proper alignment and avoiding excessive wear.
Belt Tension Gauge – helps set the belt to the correct limit so the pump does not strain excessively while rotating.
Sealant and Gasket Material – needed during the gasket replacement or resealing process so that a proper seal is formed to contain potentially leaking coolant.
Coolant System Flush Kit—consult without flushing old coolant away and replacing it with the ones specified to avoid cross-fluid damage.
Using these tools appropriately ensures that all these parameters—torque, alignment, belt tension, gasket, and coolant—are met. This may improve the system’s functionality, but more importantly, it increases the durability of the repaired components.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the main benefits of using quality auto shaft water pump bearings?
A: Considering the quality advertised, quality auto shaft water pump bearings tend to provide a number of benefits, including greater durability, lesser friction, improved seals to furnish leak-proofing, greater precision in rotation, and enhanced capacity for radial and axial load bearings. In addition, they contribute to lesser noise, greater cooling efficiency, and performance of the vehicle’s cooling system.
Q: How do quality water pump bearings affect the cooling system’s performance?
A: Quality water pump bearings facilitate precise and smooth water pump impeller rotation that provides fine coolant circulation and helps maintain the optimal temperature of the engine, which, if exceeded, could damage various components of the engine. Moreover, improved sealing helps prevent coolant losses that can significantly lower cooling capabilities and, without a doubt, damage the engine more so in a detrimental manner.
Q: What types of bearings are commonly used in auto shaft water pumps?
A: Bearing types used in water pumps are typically ball or roller bearings with two or more rolling element groups, such as single-row deep grooves or double-row angular contact ball bearings. The kind of bearing used is determined by the design and load requirements of a particular vehicle. Water pump bearings may be fitted with special seals or grease to other bearings for enhanced durability and performance on the bearing surfaces.
Q: In what ways do quality bearings impact noise reduction in water pumps?
A: Bearing quality relates to noise level because it is precision-ground to smoothen the surfaces of the inner and outer rings and raceways. This ensures that the inner and outer rings and raceways have smooth surfaces. Along with high-quality rolling elements, this minimizes vibration and friction during rotation. Quality bearings, therefore, significantly cut down operational noise emanating from the water pump, enhancing a quiet overall driving experience.
Q: What is the relationship between quality water pump bearings and fuel efficiency?
A: Well-designed water pump bearings can improve fuel economy by reducing friction, leading to greater energy efficiency in the function of the engine. Moreover, the quality bearings ensure that the effective cooling maintains the engine at a reasonable temperature so that the engine can rest at its optimal performance level, which leads to better fuel economy.
Q: What considerations should I consider for a supplier of quality auto shaft water pump bearings?
A: It is critical to consider suppliers with a history of accuracy when purchasing quality auto shaft water pump bearings. Borings sold by the supplier must be able to meet or surpass the OEM’s requirements and be of adequate quality and must form a high-level control and warranty. Besides, consider suppliers with more profound technical capability and a broader range of bearing types depending on the different models of the vehicle, as well as performance and specification documentation.
Q: In what manner do quality water pump bearings endure temperature changes as well as extreme environments?
A: Quality water pump bearings are manufactured to endure the rigorous conditions present in an engine, such as high temperatures and coolant exposure. They are made with materials and coatings that provide rust and corrosion protection. The bearings are designed to endure temperature changes, significantly expanding and contracting while remaining functional. The ability to endure temperature changes and extreme ambient conditions ensures reliable performance and durability of the water pump.







