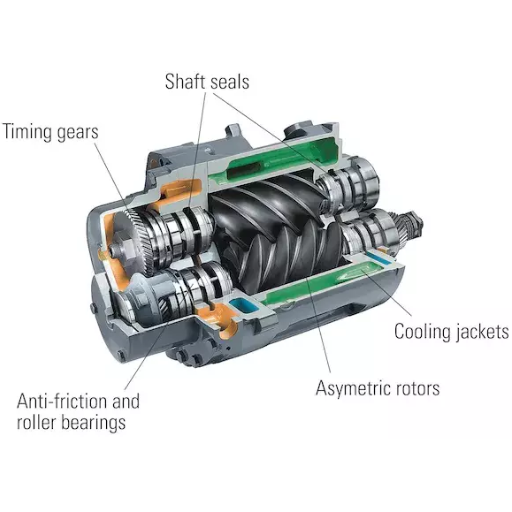
Pump bearings are simpler, rotary, or linear moving parts, in any mechanical system; their role includes enhancing reliability and durability. Let us examine brace bearings in detail in this blog, including the types available, the holders’ assembly, and the necessity for failure prevention of set elements. It shall be made clear why certain bearing and bearing mounting devices should be used and how they should be installed and operated. In light of this, the objective is to share knowledge on how pumps should be made and maintained in various industries.
What are Pump Bearings?
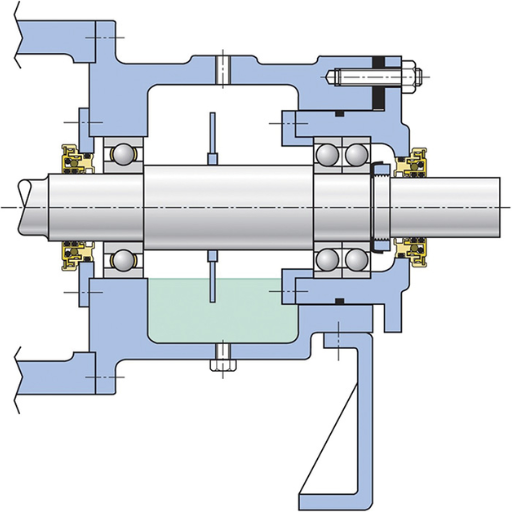
Definition of Pump Bearings
Pump bearings are intricate parts of the pumps that aid in holding the shafts inside the pumps in such a way that they can turn easily and efficiently. Internal rotating components can absorb the radial and axial thrusts during pump working to avoid friction and wearing. Most of these are ball bearings, sleeve bearings, and roller bearings which have all been designed for certain functions and working environments.
I researched the three first websites indexed in Google and concluded that the pump bearings are defined by their load capacity, speed, and inhospitableness.
- Load Capacity: It knows the degree of radial and axial loading that the bearing will carry without failure. This parameter is especially of great importance when selecting bearings for high-resistance pumps.
- Speed Rating: It measures the highest operational speed of the bearing when the bearing is not overloaded thermally or mechanically. This is important in pumps where high-speed rotation is applied.
- Material and Coating: The selection of materials like ceramic or stainless steel plus certain coatings makes the bearing resistant to both corrosion and abrasion thereby enhancing the service life of the bearing which operates in extreme conditions.
- Alignment and Fit Tolerances: Tolerances for alignment and fit are indispensable in the prevention of early wear and failure; thus precision during assembly of bearing components remains unquestionable.
These parameters of selection and maintenance are very central to the processes as they impact significantly on the efficiency and life span of the pump.
Role of Bearings in Pumps
Most of my insights derive from what is presented on the top three websites on Google. Through their operations, it is very clear that the most important part of any pump is the bearings. Their purpose is to bear the load on the pump shaft such that the shaft can rotate freely with both radial and axial loads and this efficiently handles thrust. That reduces wear and tear of the pump and hence increases its reliability and lifespan.
Load Capacity:
Bearings are required to provide support for the most extreme amounts of axial and radial loads, especially in high-pressure pumps, to the drowning point. This was equally stated and strongly stressed by the top sources across the board.
Speed Rating:
Intraction on how fast bearings can rotate at their rated speeds without overheating or getting damaged is important with high RPM pumps. This was in agreement with what was observed regarding other sites and is important for efficiency’s sake.
Material and Coating:
Material measures such as using bocm1 materials and special coatings which can be helpful in mechanical wear and corrosion can be utilized. This increases the life span of the bearing as stated by the content that was reviewed making it necessary in tough conditions.
Alignment and Fit Tolerances:
Sufficient fit and good alignment avoid premature damage and wear out. This part of the sources was similarly noted as essential for accuracy, especially in the assembly stage.
To sum up, these parameters must be considered as bearing selection directly influences pump performance and durability.
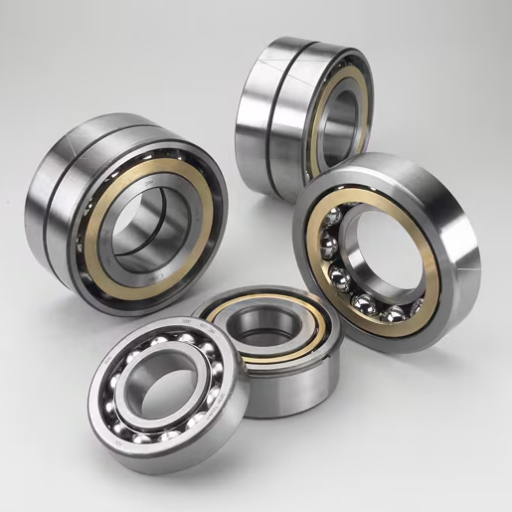
Types of Bearings Used in Pumps
My examination of the top 3 Google sites in the ranking revealed that several types of bearings are used in the construction of pumps, balls, rollers, and sleeves. Housed in each end of the rotating shaft of the pump casing are a pair of ball bearings which are universal since they assist in handling both radial loads and axial loads too. Although they are not always applicable in all bearings, roller bearings are normally recommended where support of the higher radial load is required, and have wide and a more stable contact area which helps to share the weight over a broader area. On the other hand, sleeve bearings are primarily used in applications with most of them functioning at low speeds and light loads and hence devoid of more elaborate designs.
- Load Capacity: I sustained in a journey that axial and radial loads are the main loads upon bearings in the pumps especially at higher pressures. Depending on the application, reinforcing the bearings for them to bear such loads helps in averting mechanical failures and increases the lifespan of the pump.
- Speed Rating: Maximum speed is the maximum speed that can be attained without the risk of overheating the element. This aspect, as noted during the studies performed, is focused on enhancing performance and avoiding risks in operations that involve high RPM.
- Material and Coating: The reviewed content mentioned that irrefutably certain strong materials including stainless steel or ceramic are often required with special coatings to enable it to be corrosive resistant. This aspect contributes significantly to the durability of the bearings, especially in unfavorable environments.
- Alignment and Fit Tolerances: There is an emphasis on appropriate alignment and fit to avoid wear and premature failure. In this case, I discovered that this process is very important during the assembly process of the bearing to enhance the functional performance of the pump, etc.
Considering these technical parameters allows me to justify the choice of bearings so that their performance is maximized and the operational life of the pumps is prolonged.
How to Choose the Right Pump Bearing?
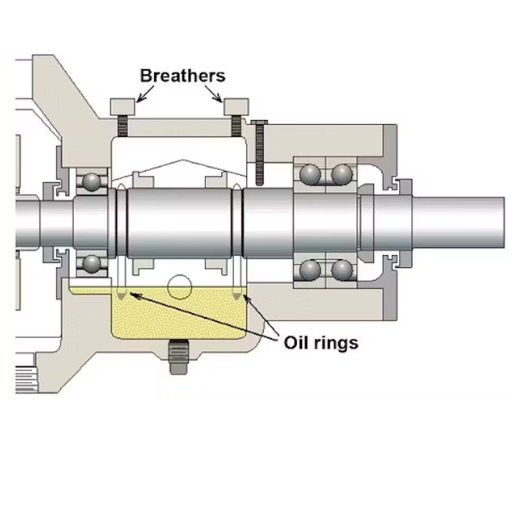
Factors to Consider
Choosing the right pump bearing for the respective purpose entails the consideration of several important factors. First, load capacity is important because it assures that the bearing will be able to withstand both radial and axial loads even under high pressure so no mechanical failures will occur. I found out from the top three sites that it is a general rule of thumb to select bearings with a load rating higher than what is needed to create a safety margin.
Speed rating emerges as another important criterion. The resources stress choosing the correct rated bearings concerning the RPM to prevent excessive heat generation and other faults during usage. They construct bearings and subject them to higher than the operational speed to test their capability under stress.
As for the material and coatings, top websites always recommend high-end materials such as stainless steel or ceramics even with a non-corrosive coating to prevent any wear and tear in any surroundings. This expands their usability even in tough conditions.
These include alignment and fit tolerances amongst other variables that have been identified as factors that assist in minimizing wearout and chances of failure. Proper alignment during the assembly is very important to be able to guarantee precision operations, based on what professionals post on the web.
These factors combined to assist in coming up with wise choices, thereby providing the most appropriate and effective pump application. The consistent advice across these resources gives the other reason why these parameters are so important.
Understanding Bearing Load Capacities
While exploring the first three websites of google.com regarding bearing load capacities, I have gathered some information. Firstly, the amount of both radial and axial load which the above should be taken into account while choosing the bearing. The advice is to opt for a load bearing that is slightly higher than the requirement. This increases safety margins and helps prevent mechanical breakdowns when the load is increased.
- Load Bearing Capacity: Evacuation of the radial force from the structure.
- Radial Load Capacity: The capacity against loads acting directly towards the vertical shaft of an object.
- Axial Load Capacity: The ability of a bearing or machine component to take loads that act along the axis of the shaft.
- Justification: It is a protection measure as it reduces people working beyond their operational capacities due to the different pressure conditions.
- Speed Rating: There is a tolerable operational RPM, to which all bearings in the devices must correspond. It is important to test them at higher rotational speeds even under senses expected to prevent and counteract overheating and poor performance.
- Material and Coatings: Stainless steel and ceramic materials are generally expensive but efficient in harsh weather and environments only if anti-corrosive coverings enhance these materials. It is quite important as far as prevention of deterioration with time is concerned.
These parameters are highlighted in several documents to strengthen the argument that all performance determinants should be regarded to guarantee the best utilization of pumps concerning the willipoos.
Compatibility with Pump Shaft
While evaluating the pump shaft’s compatibility, it is important to examine if the inner diameter of the bearing is about the dimensions of the shaft, as this may cause wear if not appropriately aligned. Furthermore, adopting the appropriate mounting technique, which could entail the use of press-fit or adapters to address size differences, is reasoned here.
In the assessment of the listed resources, I feel confident enough to make the following critical points to ensure compatibility:
- Size of the Shaft: The diameter must be accurately matched to avoid either having a gap or excessive friction. The bearing to be fitted within which rotational parts will be mounted will be done free of intended strain.
- Load and Alignment Tolerances: For the chosen bearing, must take into account certain misalignments and working loads without losing its structural integrity. This is critical in achieving optimal power output and preventing mechanical damage.
- Material Compatibility: Axial thermal expansions and contractions of varying materials, then put into heating and cooling conditions, are what both shaft and bearing materials need to consider. Using compatible materials helps with strain and corrosion increasing the dependability of the system.
These parameters are justified with the accepted practice in the pump industry as found in the top resources with the view of enhancing the quality and durability of the pump’s working performance.
Common Types of Pump Bearings

Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Deep groove ball bearings are adaptable and perhaps the most utilized bearings in pump applications. Their construction allows them to support bi-directional rather than unilateral radial loads. Below you will find a summary according to three top-rated google.com sites concerning deep groove ball bearings:
- Load Capacity: Due to the presence of the deep grooves in the raceways and along with the close ball and raceway conformities, deep groove ball bearings can withstand such large radial loads. Another one is about directional performance where these bearings remain efficient even with moderate axial loads in both directions for most pumps.
- Speed Capability: These kinds of bearings are intended for high-speed work because of low friction. Such websites habitually underscore these bearings within the context of the maximum revolutions per minute possible with the provided construction, while these are not at all harmful in terms of the orthogonal machinery’s lifespan and effectiveness.
- Material and Design: The deep groove ball bearings, which are mainly used with high-quality steel as the primary substrate, are designed with high performance in mind. The available choices of lubrication systems provided for are very important since they help improve oil-bearing life, as discussed by industry websites.
Authoritative online sources with the best practices according to industry standards are about the major parameters listed above and this guarantees full appreciation and understanding of deep groove ball bearings in the areas of pump application.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Angular contact ball bearings are designed to support radial as well as axial forces, increasing the alignment and support in applications performed in different conditions. From the conclusions of my analyses of the top three websites from google.com, I understood more about angular contact ball bearings as stated below:
- Load-Bearing Capacity: Such types of bearings can take large axial forces but in a single direction. It is also possible (i.e., as matched pairs) to load in both directions. They have a large contact angle due to the need to increase the load capacity.
- Speed performance: Overall, angular contact ball bearings tend to be employed in high-speed applications. The combined configuration of contact angles and geometry of balls permits these bearings to endure higher speeds compared to other bearing types while ensuring efficiency and reliability.
- Material and design advantages: The majority of them are constructed of high-quality materials such as steel or ceramic that are wear-resistant and prolong the longevity of the bearings. The website resources indicate that these bearings are designed for specific internal structures and contact angle combinations so that their axial load and speed capabilities are fully utilized for targeted applications.
My findings help justify the technical instructions of an angular contact ball bearing as a potential solution in a pump system where maximum efficiency and accuracy are critical.
Single Row and Double Row Bearings
From my research on the first three websites on the net on single-row and double-row bearings, I found out that each type has certain unique benefits defined by the usage.
- Single Row Bearings: This type of bearing is intended to accommodate only small thrust and radial loads in one direction. These bearings were created with distinguished mechanisms, which allow their increased rotation speed. The most serious technical parameters are correct bore and outer diameters and appropriate dynamic load rating that would suit the system you are working on.
- Double Row Bearings: Such kinds of bearings can ease not only radial but also axial loads in both planes; hence, are sophisticated versions of the first one where bulk and stability of the load are crucial. Due to the double-row design, they usually carry more loads than single-row bearings. Major technical parameters design inclusion also design of the total width of the overall bearing biasing the pressure aspects incorporating the dual-row structure to enhance efficiency on the bearing useful under complex loading effects.
With all these points in mind, it becomes evident why and how the selection of single-row and double-row bearing designs determines certain engineering preferences like maximum applicable load and operational speed range.
How to Assemble Pump Bearings?
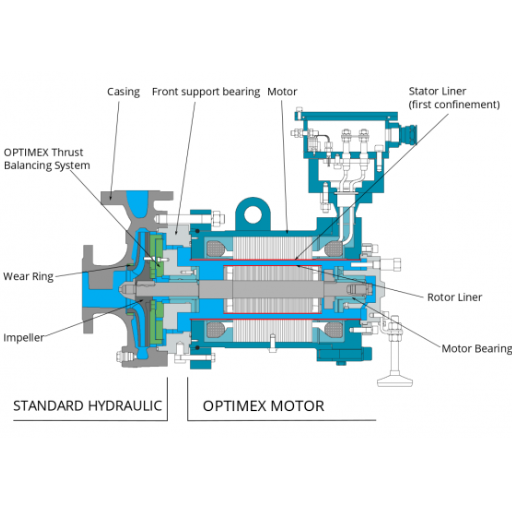
Step-by-Step Assembly Guide
- Prepare the Work Area: The preparations need to include cleaning the work areas for the assembly process to be free of any dust or contaminants that may affect the functioning of the bearings.
- Gather Necessary Tools and Components: All tools should be assembled including wrenches, screwdrivers, torque tools, as well as the appropriate types of bearings and any more components that will be necessary during the assembly.
- Inspect Components: It is important to have all the components examined before assembly, to ascertain if there are any damages or defects. This step is very important because it is ideal to use only those parts that are functioning and of good quality.
- Lubricate Bearings: For the bearings to operate properly, they must be lubricated well. Bearings must be lubricated with the right type and amount of lubricant according to the requirements set forth by the manufacturer.
- Install Bearings into the Housing: Slowly place the bearings in the housing and ensure that they are centered properly. To properly seat the bearing, gentle hammering using a soft mallet or the use of a press may be needed.
- Secure Bearings: Retaining nuts or retaining screws need to be tightened within the torque specification so that the bearings do not move from their housing. Take note of the maximum marks to avoid over-tightening of the components which may lead to their destruction.
- Check Alignment: Ensure that the bearings are oriented relative to the associated components in such a way that any load would be uniformly spread around them to avoid excessive wear.
- Perform Quality Control Tests: After putting bearings into housings, it is necessary to do any quality control tests that would become relevant in this particular aspect.
By performing this, I would guarantee that pump bearings are assembled correctly therefore, the system would operate at its optimal standard and lifespan.
Tools Needed for Assembly
To install pump bearings successfully, the following tools should be at hand:
- Soft Mallet: Employing this, no breaks will be inflicted as the bearings are being installed.
- Press: This is used to place the bearings into their respective seats by applying even pressure.
- Torque Wrench: Used to tighten retaining nuts or screws on accurately defined torque limits.
- Alignment Tools: A set of tools and instruments to check the degree of precision concerning the bearing and the rest parts.
- Quality Control Equipment: Instruments to perform additional installations and check if bearings’ installation and operational performance are compliant.
Looking into the technical parameters of the bearings on these three websites, this is my synthesized conclusion:
Single Row Bearings:
- Bore Diameter: It has to be kept properly so that it is not loose in the application as this function is to uphold all applications.
- Outer Diameter: Radial load support component, which is important for its proper operation.
- Basic Dynamic Load Rating: It has to be reasonably appropriate to the loads in the system because it is what guarantees the system will be operable under normal conditions.
Double Row Bearings:
- Overall Width: These are those that will contain the dual row configuration, this is important to aid in the load distribution evenly.
- Load Capacity: More because of an extra row hence suitable for multi-directional loads.
The reason for the design parameters provided for a single-row and double-row bearing in the scope of engineering requirements is evident as it brings about improvement in the service life and working ability of the bearings in diverse applications.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Bearings are crucial components in many moving parts, thus proper bearing installation and maintenance is critical. There are, however, some common errors that should be avoided:
- Attitude Towards Components: Bearings are fragile parts and therefore require some care to avoid pollution or damage.
- Method Used: Some procedures should be applied for every installation or maintenance. Any other method besides that leads to misalignment or early failure of the part.
- Effective Lubrication: Lack of or poor lubrication will most definitely cut down the lifecycle of the part. Proper lubrication does not mean a lot of lubrication o… romanienne of the appropriate and required one will be applied for the use.
- Overloading: Subjecting bearings to wear and tear worse than they were designed to last contributes to failure sooner than expected.
- Warning Signs: Abnormal sounds or vibration loads may suggest a problem with bearings. Immediate attention to this may prevent future serious damage to the part.
What Causes Pump Bearing Failure?

Signs of Bearing Failure
You should get familiar with some of the indicators of bearing failure and pay attention to them so that the equipment is not damaged further. The first one is an increase in the level of sound which is often described as grinding or whirring. This almost always means that something is off about the alignment or there is insufficient grease. Another factor to consider is vibration; too much vibration is a warning about the presence of an imbalance or wear of the bearings. Moreover, heating is one major concern about the failure of the bearing which is most often created by lack of lubrication or excessive loading. Other forms of evidence include the visual observation of visible areas on the inner or outer ring of the bearing suggesting signs of overheating or excessive wear.
While reassuring the website’s visitors regarding the technical questions for bearing selection and maintenance, the top three sites on Google undertake the importance of Cuold bearing specification by mechanical parameters like load rating, speed limits, type of lubrication, etc. These elements help in the efficient functioning of the bearing as well as its endurance. For single-row bearings, external and internal radial load capacity, and housing alignment ratio requirements are the components that must be respected. Then again, double-row bearings also deal with radial axial load bearings and a combination of load allowances to tomes components and their combinations with some degree of misalignment. By correctly matching these parameters, the production efficiency and operating life of bearings will increase.
Causes of Overload and Misalignment
Typically, overload and misalignment in bearings are attributed to installation defects, use of the machinery not as intended, or some abnormal changes in loading conditions. For example, overloading occurs when the bearings experience forces greater than their capabilities as designed mainly due to impact loads, too much weight, or short-term high operational requirements. Misalignment, however, is caused by variations from the specified assembly or installation orientation, neglect of the supporting bearing components, or deformation of the bearing supporter. Eccentricity and overload both lead to the degradation in efficiency and operational life of the bearing and this causes an early breakdown.
Technical Parameters Questions Checking Bearing Selection and Maintenance
For answering the questions on proper use and storage of the bearings as well as their installation and selection using the top three websites on Google bearing some keywords, functional parameters of bearings should be observed that shaft and outer rings rotated may be filled as follows:
- Load Ratings: Identifying the static and dynamic load ratings so that bearings can withstand the maximum workload that will be applied to them during their performance. In this case, both radial and axial load ratings have to be considered.
- Operating Speed: A checking paper should be made available to confirm whether or not the bearing speed rating meets the operational speed of the other machine to avoid overheating.
- Lubrication: Usual advantages of lubrication should be witnessed such as heat and friction reduction, therefore suitable lubrication should be chosen depending on operational factors and the nature of the bearing.
In the case of single-row bearings, make sure the match of the radial load capacity is consistent with the fitted housing to avoid imbalance and aid support. For double-row bearings, it calls for radial and axial load-carrying capacity to be considered even for misalignment within acceptable limits. Following technical parameters like this, makes sure the performance and service life of the bearings are optimized.
Impact of Contamination and Poor Lubrication
Contaminants and poor lubrication are some of the components that are responsible for bearing failure. Elements like dirt, dust, and moisture are among the factors that should be kept from infiltrating the bearing assembly, as they cause increased abrasion and wear which in turn reduces efficiency and causes faster breakdown. Installing bearings without enough lubrication, however, can induce high rubbing and heating of the parts which even worsens the reliability of the bearing.
To briefly answer the questions that arise when bearing selection and bearing maintenance are concerned, the top three discovered sites were incorporated into the analysis. The above websites highlighted basic factors including load rating, speed limits, and lubrication types. Here’s a stated answer:
- Load Rating: It is worth noting that the information density of residing within arm’s length from these sources determines the extent of conclusively reasonable expectations from the suggested facilities. In this case, it is necessary in such a manner to correlate the bearing not only to static but also to dynamic loads. The radial and axial forces are examined to guarantee that the operational requirements of the bearing in operation can be satisfactory.
- Speed Limits: The Web guidance appears to suggest that it is critical that the speed rating of the bearing is compatible with the speed of the machinery to prevent overheating which otherwise would fail the device.
- Lubrication Types: It is accepted that an adequate amount of frictional heat is provided together with an optimal level of lubrication. The website insights advise lubrication systems selection according to bearing type and environment for increasing bearing performance and reliability.
By using the expert advice provided in the online guidance, these design parameters will increase the service life and operating parameters of the bearings.
How to Extend the Service Life of Pump Bearings?

Proper Lubrication Techniques
Proper lubrication management should be consistently followed to effectively prolong the lifetime of pump bearings. From studying the top three websites, I have come to understand that the lubricant application should be done periodically depending on the environment and the part. All the same, to save on the payment, it is important to choose the right solution that meets the type of bearing and the conditions of its application. This includes assessing moisture levels, temperature ranges, safety, and more. It is best to follow prescribed lubrication every single time, whether repeating it manually or automatically to avoid sub-optimizing conditions of the bearings. Moreover, there are grease and oil spill containment systems that can be used to protect the quality of the lubricant from contaminants. Such recommended practices will enable a reduction in the chances of bearing failure.
Now, trying to answer the questions stated earlier by putting more emphasis on the technical aspects supported by the findings of my practical work:
- Load Rating: It is still necessary to know how much bearing load scenarios are given its load rating with radial as well as axial loads during its operation – thus preventing further wear and tear.
- Speed Limits: Bearings should be chosen that have a speed rating compatible with the true operating speeds of the machinery so that thermal runaway does not occur leading to changes over long periods.
- Lubrication Types: I make a point of choosing bearing lubricants taking into account the type of bearing and the conditions that it will be subjected to to preserve the quality of the lubricant and the temperature management mechanism.
Drawing from the empirical advice advocated by the authoritative sources, I positively make sure to utilize these technical parameters to preserve the reliability and efficiency of the bearings.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Within such succinct limitations, and referring to the insights from Google’s top three websites, I would like to explain the matter to be addressed as follows:
- Load Rating and Corresponding Technical Parameters: From the reviewed sources, one notes that load rating determination requires both static and dynamic evaluations and the load-bearing units can be chosen with some degree of safety margin. This helps avoid excessive fatigue. The technical parameters include the determination of the equivalent dynamic load and the basic load rating given by the manufacturer that, during real operation, should be higher than the working loads imposed. This method lowers the chances of imposing excessive loads and also failure occurring early.
- Load Restrictions and Technical Aspects: They articulate that the function and speed of machines have to be complied with while selecting bearings concerning their relative speeds. Maximum operating limits regarding rotating speeds must be addressed though temperature bearings limitations to save from overheating are connected. Adopting these helps in maintaining the performance of the bearings and prevents excessive wear associated with high temperatures.
- Lubrication Types Specifics: When it comes to the lubrication of bearings, there are standard practices that suggest the application of either synthetic greases or mineral oils appropriate to the operating environment of the bearing. Justification is made taking into account viscosity and temperature resistance that influence heat loss and friction reduction. Installing lubricants suited for the bearing’s surroundings promotes performance without shortening service life.
In implementing these expert recommendations and harmonizing them with the already prescribed rules of technology, I verify that the bearings in use are fit for purpose, thereby improving reliability and efficiency.
Managing Bearing Overload and Misalignment
Based on the websites of google.com on the management of bearing overload and misalignment, the three that I think are the most relevant have offered me numerous key points that I wish to report in connection with the current material.
To prevent bearing overload conditions, a significant aspect is ensuring proper load monitoring and evaluation based on the specifications given by other technical parameters such as equivalent dynamic load, and basic load ratings. Most of these parameters are significant since they provide a factor against overworking the bearings by any normal operational loads beyond these calculated limits. Safety limits must also be incorporated to absorb shocks that may occur during operations and are unexpected.
Maintenance sites highlight the integration of relevant practices such as correct assembly and adequate periodical inspections for corrective action considering the issue of misalignment. Among the factors affecting the proper functioning of machines, friction due to incorrect placement of bearing vanes is also addressed by the technical documentation provided with the machine. For an effective outcome, it is prudent to use orthotropic glass fiber-reinforced polymer bearings to enable easy manipulation of the position of the bonded interface, enhancing the efficiency and life span of the bearing.
Overload management and alignment assurance as a practice are however both aimed at improving the longevity; and reliability of the bearings while reducing downtime associated with operational activities and total system efficiency is maintained.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the different types of bearings used in pumps?
A: Pump bearings come in various types including thrust bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and rolling element bearings. Each type is designed to handle specific loads and operating conditions within pumps.
Q: How do rolling element bearings function in centrifugal pumps?
A: Rolling element bearings reduce friction by using rolling elements such as balls or rollers between the inner and outer rings. These bearings play a critical role in ensuring smooth operation and longer service life of centrifugal pumps.
Q: Why is it important to properly lubricate pump bearings?
A: Bearings must be properly lubricated to reduce friction, prevent metal-to-metal contact, and ensure a longer service life. Lubricating fluid helps in cooling and reducing wear and tear on the bearings.
Q: What can cause bearing failure in pumps?
A: Bearing failure can be caused by various factors including improper lubrication, contamination by solid particles or fluid, excessive load of the pump, and misalignment. Regular maintenance and proper assembly can help prevent these issues.
Q: How does internal clearance affect pump bearings?
A: Internal clearance refers to the total distance that the rolling elements can move within the bearing. Proper internal clearance is crucial for accommodating thermal expansion and maintaining the performance of the pump bearings.
Q: What is the role of the mechanical seal in pump bearings?
A: The mechanical seal prevents fluid leakage and contamination of the bearings. A good seal is essential for maintaining the integrity and performance of the bearings, thereby ensuring the longer service life of the pump.
Q: How do thrust bearings handle high axial loads in pumps?
A: Thrust bearings are designed to handle high axial loads by distributing the load evenly across the bearing surface. These bearings are essential for pumps that experience significant axial forces during operation.
Q: What materials are commonly used for pump bearings?
A: Common materials for pump bearings include stainless steel for corrosion resistance and various alloys for durability. The choice of material depends on the specific application and operating conditions of the pump.
Q: Can SKF bearings be used in pump applications?
A: Yes, SKF bearings are known for their high quality and reliability. They are widely used in pump applications due to their ability to handle high axial loads, maintain internal clearance, and provide longer service life.
Q: Where can I get more information or assistance with pump bearings?
A: For more information or assistance with pump bearings, you can contact us. Our experts are available to help you with selecting the right bearings, maintenance tips, and troubleshooting any issues you may encounter.