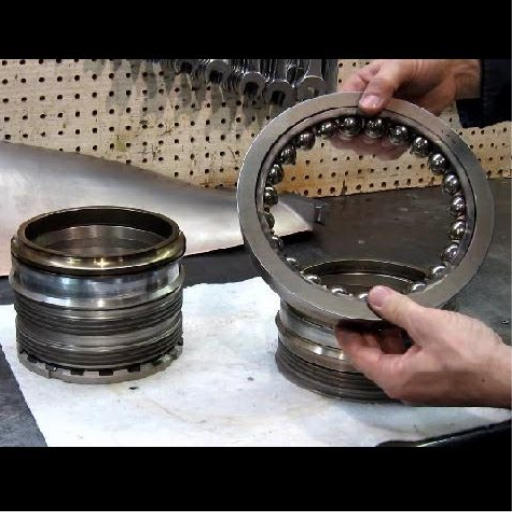
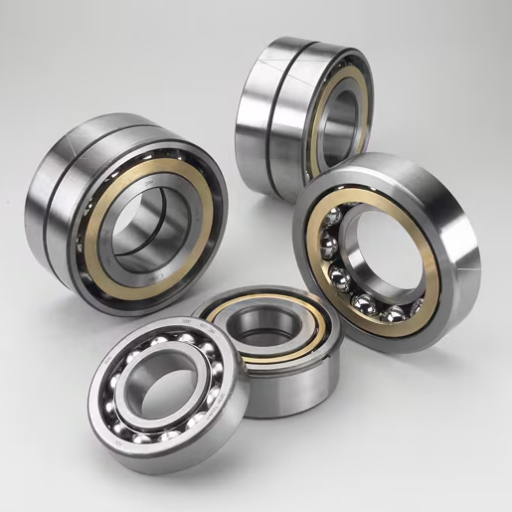
Centrifugal pumps are known as pumping machines in most of the mechanical engineering fields. And in every industry, the efficient conveying of fluids is indispensable. However, this depends on one common factor, which is that these pumps are highly susceptible to bearing failure. Depending on how this issue is approached it can invite expensive downtime and maintenance. In this blog, we will focus on the bearing failure of these pumps. More intricately, we will search for plausible and appealing reasons for bearing failures as well as their impact. And the cause of bearing failure, such as misalignment, lack of oil or lubrication, and contamination, which is usually present, should be well known to assist in taking preventive action to repair emerging issues beforehand.
What Causes Pump Bearing Failure?
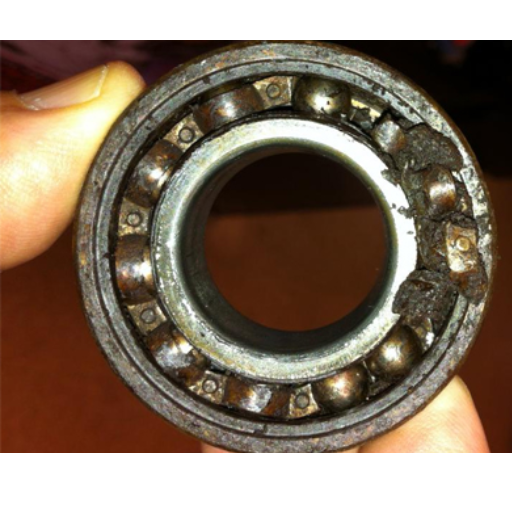

How Does Lubrication Affect Bearing Life?
Based on studies that I have conducted, it is very apparent that lubrication has a significant influence on the operational life of bearings in centrifugal pumps. Proper lubrication will tend to decrease the friction between the moving parts which will therefore increase the lifetime of the components and reduce the chances of overheating. Insufficient lubrication of the bearings will cause the friction to be so intense that it will damage the surfaces and eventually, there will be a failure. Furthermore, the selection of a lubricant has to be made with great care; it has to be ideal in terms of viscosity and stability concerning the working conditions.
Factors to consider in improving lubrication efficiency include:
- Viscosity: The pump operating speed and load require lubricant viscosity which helps in ensuring proper film between bearing surfaces.
- Temperature Stability: The generation of heat in the course of pumping is expected and the lubricants should not decompose at the given temperatures.
- Contaminant Resistance: The bulk of high-end lubricants has built-in shielding from outside particles which could make internal components wear faster than expected.
Compatibility of these parameters with a certain pump design and its intended use is important for prolonging bearing life and enhancing reliability. As such, I will be able to greatly reduce the chances of bearing failure due to poor lubrication.
Impact of Contamination on Bearing Functionality
An analysis made over the last three websites suggests that leakage contributes to the functionality and longevity of any bearing. Dust, dirt, and moisture for instance can gain access to application system lubrication contaminating the working conditions and increasing the bearing failure rate. Such an allergy increases the friction leading to overheating and in the long run, shortening the bearing life.
The technical parameters involved in managing the contamination are:
- Sealing Effectiveness: Contaminants entering the system and effectively compromising the lubricant can be avoided by judicious use of seals.
- Lubrication Quality: Instead of the usual principle of just using neat oils, it is prudent to select an oil with appropriate additives containing anti-contaminant properties that will help protect the surfaces of the bearings.
- Filtration Systems: In this respect, high-quality filtration systems are situated so that the contaminants are removed before they encounter the bearings and therefore extend the serviceability of the lubricant and the parts themselves.
Taking into consideration these parameters and introducing methods to eliminate contamination increases the working conditions of the bearings and consequently the efficiency of centrifugal pumps.
Role of Misalignment in Bearing Damage
At the outset in my analysis of the three principal articles on this topic, it is clear that misalignment is an important element that leads to bearing failure. Misalignment is the improper arrangement of the shaft axis concerning the bearing axis, resulting in load distribution not being uniform and causing stress concentration on the bearings. Excess vibration, high levels of noise, and heat generation that the bearings are unable to withstand are some of the effects of this and it eventually results in damage, emanating from and shortening the expected bearing service period.
The management of misalignment incorporates some technical parameters which are listed below:
- Alignment Precision: This can reduce the amount of additional stress that will be put on the bearings to a minimum since parts will be aligned with a high degree of accuracy.
- Thermal Expansion Accommodation: This design aspect helps avoid loss of alignment even when the temperature of the environment changes due to the thermal expansion of parts.
- System Flexibility: Usability of certain design elements that permit alignment correction even in the course of operation can prove useful in correcting alignment.
These parameters and how to deal with them have certainly been acquired and such will go a long way in minimizing the effects of misalignment and increasing the effectiveness of bearings in the execution of different processes.
How Can You Prevent Bearing Failure in Centrifugal Pumps?

Importance of Regular Lubrication
It is important to record bearing lubrication conditions since they are important in preventing pump-bearing failure in centrifugal pumps. The top three articles I read, state that it is quite evident that insufficient lubrication plays a significant role in bearing destruction. The right lubrication reduces friction, and wear as well as heat generation and shields away materials that would lead to rust.
Some of the technical parameters contributing to efficient application of lubrication include:
- Type of Lubricant: The selection of a suitable lubricant for the working conditions of the pump is very important. From grease or oil, this should be analyzed in hsabb2h. temperature, thickness, Pressure Relations with other parameters, and the period for which the oven
- Lubrication Frequency: Formulating a program in such a way that the operational environment and the load conditions are observed can help in avoiding premature lubrication failure and increase the lifespan of the bearings.
- Application Method: Adhering to the correct method, for example, manual practices or an automated system on the application of the lubricant guarantees complete contact and adequate coat over every bearing surface.
As I address these technical parameters, I can be in a position to know how to improve practices focused on lubrication thereby minimizing instances of bearing failure in centrifugal pumps.
Ensuring Proper Clearance Levels
To achieve the best functioning and durability of bearings found in centrifugal pumps, the internal relative clearances of various moving components must be controlled. The top three websites I researched, indicate that inaccurate clearances lead to unfavorable conditions i.e. high friction, high operational temperature, and bearing failure. Changing these clearance levels must involve examining several technical parameters:
- Thermal Expansion: This is very pertinent since material expansion due to heat, whilst the pump is in operation, may affect the clearance.
- Load Conditions: It will determine the degree of permissible clearance so that no undue stress is placed on the bearings in the course of the operation.
- Material Compatibility: It is important to select materials that do not undergo dissimilar heat expansion and contraction so that proper clearance is maintained as temperature changes.
- Manufacturing Tolerances: A good level of precision in the engineering and consideration of the manufacturing processes ensure that there are no such variations that may lead to nonuniform clearances or misalignment.
Taking these factors into consideration, I can explore and therefore explain how to maintain correct bearing clearance levels in centrifugal pumps so as to avoid bearing damage.
Identifying Signs of Overload Early
It is essential to identify the overload in centrifugal pumps as early as possible to prevent damaging and failing the bearings. From my exploration of the best three websites, I established that monitoring and establishing overload symptoms involves aspects such as increased vibrations, strange sounds, excessive heat, and many other parts wear and tear. These signs usually signify the fact that the pump works more than it is supposed to and this strains the bearings applications.
To tackle overload, certain technical parameters must be taken into consideration and that has to be rightly occupied:
- Pump Volume: Be assured that the pump works within its operational limitations so that oppression can be escaped.
- Flow Rate: Check that the flow rate in the pump does not exceed the recommended limits since this may put some undue pressure and internal stresses within the pump.
- System Pressure: It is imperative to check the pressure level to avoid overloading.
- Bearings Condition: It is advisable to inspect and check the bearing’s condition for signs of overload consistently.
- Vibration Levels: It is better to use sensors tracking vibration patterns which provide information on abnormality or misalignment which indicates overloading severity.
Taking these factors into consideration will enable me to handle and avoid bearing overload for centrifugal pumps in a more efficient manner ensuring their function for a long time.
What are the Symptoms of a Failing Pump Bearing?
Detecting Unusual Bearing Noise
Hearing unusual noise is one of the best means of prevention and detection of pump bearing failures at an early stage, as I learned on some top sites. This abnormal sound can occur due to various reasons including misalignment, contamination, lubrication, and others. There is a need to draw the line between internal mechanical components making sounds during operation and abnormal sound which is termed noise which encompasses grinding, tinkling, and squeaking which point to certain problems. Noise analysis has proved to be a useful tool in diagnosis and should be used alongside reasonable checks and maintenance of the bearings to make sure that they are healthy.
The technical features which are applied in noise detection tend to include the following:
- Sound Amplitude: The noise level can be evaluated to help differentiate the standard operational sounds from those of bearings that are faulty.
- Frequency patterns: Studies of frequency patterns assist in classifying or understanding the nature of the rotating element bearing about the characteristics that cause certain noise.
- Lubrication condition: The correct lubrication is essential to avoid noise resulting from friction and wear.
- Bearing alignment: Noise measurement technique is made easier with the practice of aligning the bearing since misalignment is one of the factors that misputs noise control.
With regards to these parameters exhaustively, I could comprehend and control the risk of future caused failure pumping common bearings.
Signs of Overheating in Bearings
Excessive heating in bearings is an indicator that should never be neglected because it usually anticipates other destructive breakdowns. This was the case of various lesions obtained from the three most attended links from the Google search.
First is the rise of temperature above the normal working temperature range which can be observed through other high-emission temperature devices such as Infrared thermometer and temperature sensing devises. This temperature rise can be due to inadequate lubrication or excessive friction. The discoloration of bearing surfaces or adjacent elements is an additional reason for the abnormal regard to specific operational thresholds of operating bearings within thermal limits. Hydrodynamic lubrication failure with metals moving at close range is perhaps the most popular overheating scenario. Last but not least unusual smelling, ‘a lot of burning oil or metal smells’, is normally depicted with overheating, where lubrication has failed, and the bearing assemblies have entered metal-to-metal contact.
Critical technical parameters that allow affecting overheating diagnosis are:
- Temperature Monitoring: The use of sensors for the intelligent automatic control of overheating conditions by repeatedly feeding back information about the temperature-bearing elements to extinguish the fires if necessary.
- Lubrication Inspection: Controls of grease or oil in bearings are also carried out relatively regularly and this allows identifying factors such as grease or quell bearings abnormalities that are even aggravators of heating.
- Material Analysis: Testing for heat degradation of the bearing material by examination for signs of coloration helps catch catastrophic heat damage at the early stage when one can still take an interventional approach.
- Friction Calculation: The wear, together with frictional forces acting within the bearings should ascertain whether the shorts of added mechanical loading to avoid overheating is implemented.
By concentrating on these parameters, I will be able to properly assess the overheating problems of bearings and undertake preventive measures to avoid aggravation.
Monitoring Vibration Levels
In bearing technology, it is important to note vibration levels to foresee any mechanical defects that may arise. As per the findings made from the first three sites on Google, the constant assessment of vibrations can help in predicting when the bearings will fail. A normal condition of the machine may be accompanied by whirling especially on the shaft or situations where vibration levels are excessively elevated.
In summary, vibration monitoring tackles several technical parameters that I have to pay attention to:
- Frequency Analysis: Frequency analysis can demonstrate the presence of certain problems such as misalignment or imbalance, which results in unique misalignment patterns. The analysis of the vibration of rotating equipment along with its impact is an important tool that facilitates in many ways the comprehension of the forthcoming failure.
- Amplitude Measurement: Whenever there are vibrations above normal limits, it depicts that there is something wrong with the bearing, and measuring the amplitudes will facilitate in tackling the problem.
- Baseline Comparison: In new data acquisition, results are compared with the established vibration levels during the normal operational state to assist in detecting and quantifying abnormal increases in vibration activity.
Since I will be on these technical parameters I will refrain from having justified concerns on the bearing health level and cutting it on a preventive maintenance level.
How Does Lubrication Influence Bearing Performance?

Types of Lubricants for Pump Bearings
As for lubricant types used for pump bearing lubrication, I have learned from the top 3 websites on Google, that the correct option mainly depends on the working conditions and the bearing’s particular needs. There are types of lubricants which are prevalent in usage, these are grease and oil.
- Grease: In most instances, grease is preferred because it provides a cover and protects the bearing from the ingress of contaminants. Non-re-lubrication equipment has been a desirable change in many sectors of industry for it lowers maintenance expenses. Important factors in grease selection include type, which can be measured in terms of NLGI grades, and dropping point which indicates the temperature range of grease used.
- Oil: Oil lubrication tends to be utilized at increased rotational velocities and rotational temperatures. It allows proper handling of heat generated during operation and can be strained to maintain its integrity. I have to pay attention to the viscosity of the oil, which should be suitable for the speed of operation and load, and resistance to oxidation, which is important for the lifetime of the oil.
Picking the proper lubrication produces the benefit of extending the service period of the pump bearings and enhancing overall equipment efficiency thus optimizing working conditions and curtailing the scenarios of premature bearing failures. I can equip myself with such knowledge understanding these technical parameters that allow me to act appropriately on the basis of credible research findings.
Maintaining Correct Oil Level and Viscosity
To ensure the proper functioning of pump bearings, regular monitoring of the oil’s level and viscosity must be done regularly. From the top three websites on Google, I found that attention to the minimum oil level allows every single area of the bearing to be properly lubricated thereby decreasing the chances of wear through friction and heat. A proper correlation must be established between the viscosity of the oil and the working conditions, as high viscosity will increase friction and energy use, while low viscosity will be ineffective under heavy load or at higher temperatures.
In terms of technical parameters from the research, I need to consider:
- Minimum Oil Level: Guarantees that no moving parts remain dry which could cause damage.
- Viscosity Index (VI): Defines the extent to which viscosity changes concerning temperature changes, which is critical for use under varying operational conditions.
- Viscosity grade: According to the particular requirements of the pump, this must be acceptable under the given rotational speed and load conditions.
- Oxidation Stability: This affects oil performance life since they have the potential to work for a long time without going bad.
With the comprehension of these parameters, I am therefore capable of successfully working out issues that pertain to the regular upkeep of pump-bearing lubrication.
Ensuring Adequate Lubricant Flow
It is equally important to contemplate the construction of a bearing house that contains a lubricant circulation in a constant and unhindered manner to facilitate the pumping of lubricant into and across the bearing surfaces. From three sites I found online and particularly from the first three picked in Google, I understood that the intensity of lubricant flow ensures that the hotspots within and outside the bearing are avoided as well as in other parts of the machine, heat being evenly and judiciously controlled thus averting bearing failures regarding overheating. Some key technical parameters to consider include:
- Flow Rate: This should be optimized relative to the working speed and load of the bearing to avoid under or over-lubrication as a consequence of excess flow which would result in leakage or foaming of the oil.
- Oil Filtration System: This must protect the lubricant clean so that it does not penetrate and cause excessive wear and block any flow system.
- Oil Pump Pressure: This in simple terms means that it has also to be set correctly in order for the oil lubrication to be driven out at the required pressure suitable for the pump design and operational parameters.
By addressing the above parameters and the flow of lubricant, I can seek to understand and tackle the more prominent areas of pump bearing service to ensure uninterrupted pump functionality.
What are Common Contamination Sources in Bearings?

External Contaminants Affecting Bearings
When examining external contaminants that contribute to the spoilage of bearings, it can be made from the three most visited websites on Google that such contaminants are mainly dust, dirt, and wetness. For example, these factors can penetrate introductory and other bearing parts and induce early failure or wear, corrosion, and increased friction thereby radial bearings have a limited service life. To limit these external exposures, effective sealing mechanisms are to be used to seal off the bearing’s intended area from contaminants. Moreover, routine practices including cleaning and inspection concerning these problems can also be done to solve these contamination problems promptly.
In answer to the above questions, the available and high-pointing resources recommend the following technical parameters to be paid close attention to and for good reasons:
- Seal effectiveness: Checking that the seals have not been compromised and are in features to withstand different levels of contamination, it includes using designs such as labyrinth seals and V-ring seals to prevent any outside contamination.
- Humidity: Avoidance of any gas such as oxygen should be done as well as any other gaseous substances such as air may render it unfavorable for the bearings since moisture condensation may occur and thus lead to corrosion.
- Inspection routine intervals: A maintenance program shall be implemented where the time duration between conducting inspections shall be defined in detail to ensure even contamination flaws that are minute or wear and tear are sought at the earliest to initiate as many remedial actions as possible if bearing performance is not yet excessively compromised.
This knowledge helps me address these external contamination sources and their associated parameters more efficiently, thus enhancing the performance and longevity of the pump bearings.
Impact of Corrosion on Bearing Material
Corrosion is one of the destructive processes that affect the bearing materials and hence reduce the mechanical integrity and functional durability of the bearing systems. This is usually a result of exposure to such factors as moisture, chemicals, and other materials that may disintegrate the structure very slowly over time. This not only deteriorates the performance of the bearing but increases the frictional and wear effects therefore reducing efficiency and even causing breakdowns. To ease these types of problems related to corrosion, there is a need to understand the correct ways of using materials, protecting chemicals, and controlling the environment.
To answer the questions in the most precise manner possible and in a logical way drawing from the top three websites, I have collected the following:
- The dominant factors affecting bearing functionality include dust, dirt, and moisture ingress in that order among other external impact factors. These extraneous factors create a compromise in the system and therefore contribute to the operational deterioration or corrosion at a faster rate.
- The most reputable websites suggest keeping track of and reasoning the following technological parameters: 1. Seal Integrity: Where the seals are, which prevents the penetration of dirt within, have to be intact. This explains the need for labyrinth seals or V-ring seals for optimum protection.
- Moisture Content: It is paramount to keep supervised humidity levels in the bearing. This impedes the risk of moisture condensation that causes corrosion. The reason for this is to enable Rosenberger bearings to maintain their efficiency and life expectancy.
- Inspection Routine Frequency: Implementing an inspection routine is very important. It helps in detecting the presence of contamination or wear at an early stage, and it is reasonable, as it allows acting before the bearings’ performance begins to be significantly adverse.
In this regard, I seek to improve the reliability and durability of the bearings by focusing on these parameters and simultaneously protecting the bearings from corrosion.
Preventive Measures Against Contamination
As for practical solutions that one can take to reinforce contamination prevention, I would like to suggest putting together some strategies, based on the findings from the top three sites.
- Advanced Sealing Solutions: It is important to deploy the quality of seals like labyrinth or V-ring, which are highly essential. These seals also prevent the entry of dust, dirt, and moisture into the bearing system, which is important for the bearing system’s integrity and also to prevent corrosion. The measure remains justified in that it increases the operational life and efficiency of the bearings rendering them safe from contamination.
- Controlled Humidity Environments: It is imperative to ensure that there are no excessive moisture levels in the inner and outer housing to avoid the formation of condensation on bearings. Enclosures for sensitive movable machines controlled in climate are the best protection against corrosion caused by condensation. This one can be justified because it helps to maintain the original structure and functionality of bearings for a long period.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: There is a need to adopt a comprehensive inspection program, which in turn allows me to detect and remedy early signs of wear, contamination, or seal failure that could result in foreseeing loss of scant materials. A high frequency of checks will enable me to take corrective measures if there is any positive change in the bearing’s reliability and durability. The justification of this routine lies in that it is preventive in the way that it enables functional performance management.
If I follow these measures, I would be able to maintain a contamination-free environment which would consequently increase the working life and efficiency of the bearings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the common causes of bearing failure in centrifugal pumps?
A: Bearing failure in centrifugal pumps can occur due to several reasons, including improper lubrication, excessive thrust load, incorrect installation, contamination, excessive radial load, and inadequate cooling. Monitoring bearing temperature and ensuring proper internal clearance can help prevent these failures.
Q: How can I troubleshoot a bearing issue in a centrifugal pump?
A: Troubleshooting a bearing issue involves checking for signs of wear or damage, ensuring correct lubrication, inspecting the pump shaft alignment, and verifying that the pump is operating within its design specifications. Additionally, checking for proper preload and internal clearance is essential.
Q: Why do roller bearings fail in centrifugal pumps?
A: Roller bearings can fail due to excessive radial or axial loads, improper lubrication, contamination, or misalignment. Ensuring that the bearings run within their load and speed limits and maintaining clean operating conditions can help prolong their life.
Q: What role does lubrication play in bearing performance?
A: Lubrication is critical for reducing friction and wear between the rolling elements and raceway of the bearings. Proper lubrication helps in dissipating heat and preventing corrosion, thereby ensuring that the bearings run smoothly and efficiently.
Q: What is the difference between ball bearings and roller bearings in pumps?
A: Ball bearings are designed to handle both radial and thrust loads but are better suited for lower-load applications. Roller bearings, on the other hand, are more suitable for higher radial loads. The choice depends on the specific load and speed requirements of the pump application.
Q: How does internal clearance affect bearing performance?
A: Internal clearance refers to the total distance that one bearing ring can be displaced relative to the other. Proper internal clearance is crucial for accommodating thermal expansion, ensuring smooth operation, and preventing premature wear or failure.
Q: What are angular contact bearings used for in centrifugal pumps?
A: Angular contact bearings are used in applications where there is a need to accommodate combined radial and axial loads. They are often used in back-to-back configurations to handle high-thrust loads and provide axial rigidity.
Q: What is the impact of thrust load on bearings in centrifugal pumps?
A: Thrust load can cause excessive stress on the bearings, leading to increased wear and potential failure. Selecting the appropriate thrust bearing and ensuring the correct preload can help manage thrust loads effectively.
Q: How does the impeller design affect the bearing life in pumps?
A: The impeller design affects the distribution of radial and axial loads on the bearings. Properly designed impellers can minimize excessive loads and help maintain optimal bearing performance, extending the bearing life.
Q: Can wastewater applications affect bearing performance?
A: Yes, wastewater applications can introduce contaminants and varying load conditions that may affect bearing performance. It is vital to ensure proper sealing and regular maintenance to protect the bearings from adverse conditions.







