For every person, the DIY projects might be quite different. It could be straightforward for a seasoned mechanic, such as changing the oil. For a car modification enthusiast, it can be modifying the air suspension system. The difference between the two is undoubtedly the experience. However, one tool that could make a world of difference is the water pump bearing puller. Now, it does not matter what type of project you are taking on because, with a bearing puller, even the most tedious jobs can be accomplished without hassle. This guide will provide complete step-by-step directions on using a water pump, the ideal vehicles for the bearing puller, and the advantages of the bearing puller. Last but not least, once you are done reading this article, you will feel confident enough about taking on such a comprehensive automotive task.
What is a Water Pump Bearing Puller, and Why Do You Need One?

Understanding the Purpose of a Water Pump Bearing Puller
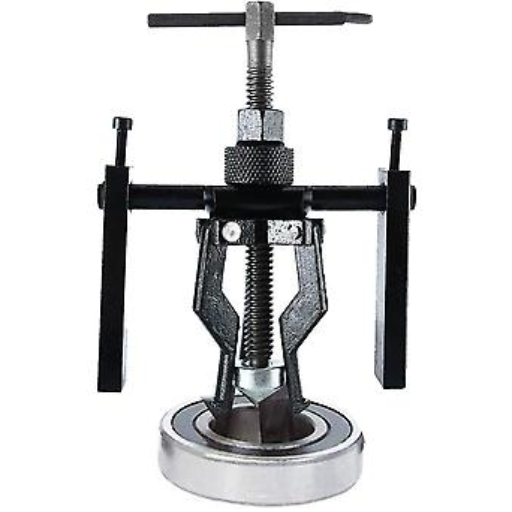
A water pump bearing puller can be defined as a tool that aids in extracting a bearing from a water pump without damaging the pump. Spare parts of a bearing that have been damaged or worn out affect the water pump’s performance. This may result in decreased performance, overheating, and total pump failure. With the help of a puller, the extraction process is more manageable and helps apply controlled force to do so, decreasing the chances of damage to the pump.
Material: Such devices are made up of high-strength steel or alloy, which adds endurance and wear resistance.
Compatibility: Such devices are compatible with single or specific water pump models or bearing sizes, so always ensure the Puller can fit your vehicle.
Maximum Load Capacity: The device should be able to use the amount of force required for extraction without getting bent or wrap around due to pressure, such devices can withstand from 2 tons of force to 5 tons depending on how much the respective application would tolerate.
Clamping Range: Such dimensions are defined in millimeters or inches regarding the seventeen water pump bearing pullers.
To conclude, using a water pump-bearing puller helps in the smooth extraction of a water pump, which increases the lifeline of such pumps and helps keep the vehicle’s performance from degrading.
Types of Bearing Pullers: Mechanical vs. Hydraulic
When selecting mechanical and hydraulic bearing pullers, it is essential to consider the type that most suits the specific demands of the application and the technical parameters. Here is a quick summary depending on their characteristics:
Mechanical Bearing Pullers: These tools require physical strength to pull the bearing off, which means they are used manually. It is effective for kinematic or simpler operations using small-sized or limited bearings, where the required number of steps and the actuation force are insignificant. Depending on the type, these models usually have a clamping range between about 10-200 mm. They are relatively cheaper but can have difficulty working under high-force situations owing to the effort involved.
Hydraulic Bearing Pullers: They perform the opposite function of applying high force on large-sized bearings using hydraulic power for tasks that are hard to reach and require minimal effort. They effectively pull large or oversized bearings, which are tricky to remove as they might be glued around the edges. They usually have a Unified claw force capacity ranging from 5 to 100. tons and, therefore, can be used for industrial purposes, of course, with appropriate sizing and specifications of the pullers. A great variety of these large bore pipe fitting pullers are characterized by the adjustable clamping range, for example, 50-500 mm range.
Adjusting the type of puller fitted to bearings optimizes their performance. This enables efficient bearing removal while reducing damage and strain to internal and external tools and machines.
Key Features to Look for in a Quality Bearing Puller Kit
Force Capacity and Durability: Ensure the bearing puller kit can withstand the required application force. For heavy industrial work, choose kits with a range of 5 to 100 tons. High levels of alloy steel improve durability and fight wear, which is prominent in high-torque conditions.
Adjustable Clamping Range: Pick a kit that includes pullers with a clamping range of 50-500 mm. This range is suitable for some bearing sizes, giving the kit a better chance of being versatile. This feature allows you to repair a broader range of machines and parts.
Ease of Operation: Puller kits should possess ergonomic handles or include a hydraulic machine since it would be easier to operate. Self-centering jaws are highlights since they assist with the extraction surrounding them by not having too much low or high precision.
Versatility: Buy kits with different jaws and hydraulic pumps as attachments, as they tend to be versatile. Versatile kits are perfect for various industries’ wide expanse of extraction tasks.
Safety Features: Overload protection in hydraulic systems and other predefined safety features are essential, so you do not have to worry about tool damage or personnel accidents. This is even truer when using high-pressure applications.
Portability and Storage: A sturdy and strong sponsored storage case would be a great addition as you could easily transport the tools to perform numerous job tasks without spending too much.
Keeping these features in mind, you should be able to pick a puller that is both technically and sustainably efficient and safe to use, thus giving you a more efficient working speed.
Lorem Ipsum Lorem Ipsum
Step-by-Step Guide: Using a Water Pump Bearing Puller Effectively

Preparing Your Workspace and Gathering Necessary Tools
Organizing workspace properly: First, remove anything that disorganizes the workspace. A flat workbench holds the water pump while taking the bearing out. Visibility is also critical to ensure safety and accuracy.
Use appropriate gear for safety: Potential problems can occur, so for safety purposes, electrodes, gloves, safety glasses, and shoes with steel toes must be worn.
Collect the exemplary apparatuses:
Bearing puller water pump set: Make sure it is appropriate for your type of water pump. Adjustable designs made of the best-quality steel would be ideal.
Torque wrench: This will be needed for the reassembling process. Ensure it can supply the correct torque, which is 10 – 150 ft-lbs, depending on what the manual says.
Hex or Allen wrenches: These might be required to unscrew the built-in parts of the water pump.
Lubricant: It is a noncorrosive fluid that is used in the process to lessen friction
Marking Tools: According to how the component is marked, its reassembling can be precise; this is why chalk or other markers should be used.
Removing the bearing should be straightforward if all these tools are handled correctly and these techniques are appropriately applied.
Removing the Water Pump and Accessing the Bearing
Draining the Cooling System: Follow the initial steps to avoid removing the water pump. Ensure that the system has been completely drained. The standard coolant capacity for most cooling systems is 1.5 to 3 gallons.
Removing the Water Pump Elements: A drill machine can safely remove a pulley belt that connects several wires to a water pump. Marking tools can also help adequately reattach parts that need to be removed. Pulleys can withstand bolts of about 15-25 ft-lbs, which are assumed but should be confirmed by the threats.
Detaching the Water Pump: Release the water pump from the water system using appropriate tools and removing its bolts. While extracting the gasket or seal, do not strain yourself too much so that you hurt the surrounding areas. The pump bolts which hold the pump in place usually have a pressure in the range of 10 to 30 ft-lbs according to the pump…
Bearings Access Management: Remove the water pump, search for the bearing, and remove it. Wear protective gloves while unscrewing the bearing puller, which needs to be placed in the correct alignment and direction. Since the bearing and the pulley wear out over time, check the housing area before moving ahead.
Being careful and ensuring all parameters are correct ensures safety while performing complex multi-step tasks.
Proper Technique for Extracting the Bearing Without Damage
To get the lever off while minimizing the chance of damage, please accomplish the following procedures:
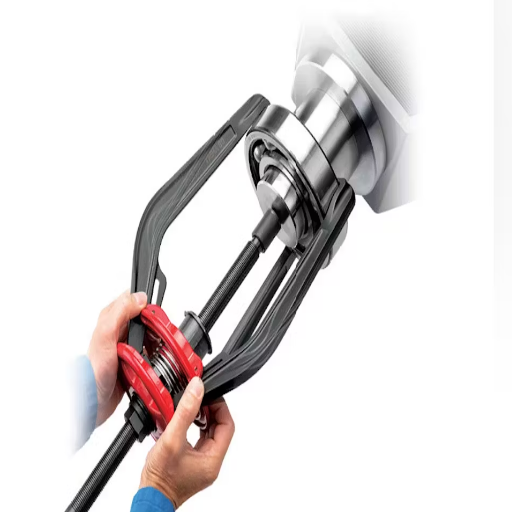
Find a Suitable tool: Get a bearing puller appropriate for the bearing type and dimensions. For the sealed bearing, be sure the tool grips the outer race firmly without cutting the seal.
Pulling force has to be applied evenly: Adjust the puller to give a bearing puller force directed in the same axis as the bearing housing puller. If the force is uneven, the bearing may be distorted, or the housing may be damaged.
Progressive removal of the bearing: Gradually tighten the puller, bearing in mind that moderate forces have to be applied so that the bearing can gradually have a slow moderated force put on the bearing to avoid jerking out, which increases the chances of cracking or bending.
Wash and scrutinize components: After removing the bearing, look at the mounting area to determine whether debris, corroded and wear particles, or any tarnished areas of the seat for the bearing. Make sure the place for the bearing is dry, tidy, and in good condition before inserting a new one to avoid the risks of any unwanted effects or interactions of bearing seating.
By adhering to these justified technical parameters, you also manage to stop the risk of failing mechanically while operating a safe and ecologically recovering.
Common Challenges When Using a Water Pump Bearing Puller and How to Overcome Them

Dealing with Stubborn or Seized Bearings
Working with seized bearings can be frustrating because extracting them without damaging the bearing or other components is difficult. My most proud method for removing a bearing is systematic. The first step is to apply a penetrating lubricant to loosen corrosion around the bearings. The only thing required here is patience, usually around ten to fifteen minutes. However, if the bearing is still stuck, I like to apply heat to the surrounding area. Applying heat causes metal to expand, which can help free up clinched bearings.
It is always imperative for people to follow specific guidelines, even when dealing with technical aspects. Some of the things I always keep in mind while extracting bearings include:
Application of Lubricant: An appropriate penetrating lubricant ensures the materials do not suffer from chemical corrosion.
Heating Limitation: Any heating concerning bearing extraction should only be done within the range of 200F-300F, or there are chances of weakening the metal.
Puller Alignment: It is always advisable to double-check that the puller arms are correctly adjusted to the pullers and capable of distributing equal directional forces to the components to avoid excessive stress on the bearing and its seats.
These steps would minimize any undesired equipment damage or injury for the operator while allowing for the safe and quick removal of the bearings.
Avoiding Damage to the Pump Housing or Shaft
To avoid harming the pump housing or shaft during maintenance, consider these essential procedures:
Assign Appropriate Tools: Use appropriate tools for the pump model being worked on and avoid using improvised tools because this emphasizes uneven pressures, which can result in displacement or damage.
Support Proper Torque Setting: Follow the manufacturer’s specific torque values when assembling or disassembling. Too much torque can stress the shaft or housing, while too little might cause the components to not fit well or sweat to leak. For example, use a calibrated torque wrench to tighten bolts to within ±10% of the specific value.
Curb Shaft Damage: Always ensure the shaft is adequately supported and horde during movement to reduce the chances of bending or scratches to any part of the shaft. Also, make sure to incorporate protective sleeves where necessary.
Always Check Casing Condition: Check the pump casing for signs of cracks and corrosion before the pump is taken apart. If any flaws are found, it is wise to check the manufacturer’s subsisting tolerances for permissible figures. Change disintegrated house components and sustain the shaft/radius integrity.
Ensure Parts are not Overheated: It is essential to avoid overheating parts, for instance, when heating components to relieve tension, restricting the temperature not to exceed 300 degrees Fahrenheit (149 degrees Celcius).
Alignment Checks: During reassembly, the shaft and the housings are in the correct position so that distortion and vibrations are not generated during use. Use precision feeler gauges or laser alignment tools as appropriate checks.
These steps guarantee the integrity of pump parts and keep the system operating, thus minimizing the costs of repairs or replacements.
Troubleshooting Misaligned or Slipping Puller Jaws
The harm caused to the efficiency of the maintenance work occurs regularly because of the puller with jaws slippage or misalignment. The following general procedure can help in addressing this issue:
Jaw Checking: Determine whether the jaws are cracked, deformed, or worn out. If they are severely damaged due to wear and tear, they need to be replaced to maintain the object’s reach during the process.
Jaw Correct Positioning: Always check that all jaws are placed evenly and symmetrically on all sides of the part that needs to be extracted. Jaw misalignment encourages slippage/jaw slippage and uneven pressure factors.
Jaw Clamp Tightening: Ensure that the puller jaws are injured enough. A low clamping force can lead to slippage, while too much can worsen the puller or the piece.
Grease Applying: Spread grease on the moving parts of the puller, such as the screws as well as the pivots, to stop the lagging that can affect lifting on the hands. NLGI grade two is a good option as it is made from grease.
Tool Size Checking: It is essential to determine whether a proper-sized puller is used for the job. Too short or too large a puller can prevent the two from pulling the object correctly.
Implementing the measures mentioned while considering the technical parameters will compensate for the various factors and enable the perfect functioning of the puller system, resulting in a safe and suitable work procedure.
Maintenance and Care Tips for Your Water Pump Bearing Puller
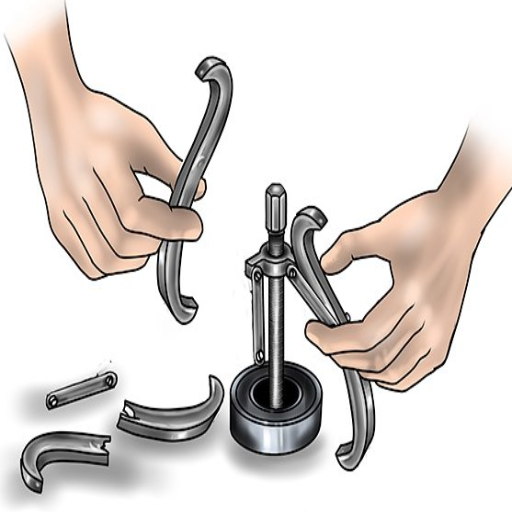
Cleaning and Lubricating Your Puller After Use
Cleaning and lubricating your water pump-bearing puller regularly after every use will guarantee optimal operation and prolong the tool’s lifetime.
Clean Thoroughly: Scour the puller components with a clean cloth and an appropriate solvent, such as isopropyl alcohol, a degreaser, or both, to eliminate dirt, grease, or debris. Preferably, use stronger solvents first. Ensure all residues are thoroughly wiped off to avoid wear or corrosion.
Inspect for Damage: Inspect whether the screw, arms, and pivoting points have any signs of wear, cracks, or distortion. If any mechanical part looks damaged, consider replacing that component before the subsequent use.
Lubricate Moving Components: With components that are threaded or pivot-based, utilize a high-quality lubricant, preferably NLGI grade 2, to ensure operating efficacy – this also assists with friction management. Only use adequate lubricant since excess grease and other lubricants will enable dirt collection.
Guaranteed performative aid is achieved with these steps, and one must remind oneself to keep the tool clean and lubricated to prevent undue damage, even several years later.
Proper Storage to Prevent Rust and Wear
One of the most important goals concerning the maintenance of these tools is preventing rust and wear, after all, once tools rust or are worn out they are rendered useless and would need to be thrown or replaced. The following points will ensure that the tools last longer:
Keep in Dry Place: Humidity is a sure way to guarantee that rust forms. To combat this, keeping all tools in an arid area is essential where humidity never surpasses 50%. To achieve that, a dehumidifier or silica gel should be used.
Apply Treatments to Prevent Corrosions: To prevent red rust from forming on the tools when stored, all metallic surfaces should be sprayed with a light coating of rust-preventive spray or oils such as Wd40.
Proper Storage of the Tools: Store away the tools in toolboxes, cabinets, or racks so that there is no metal exposure to moisture. This is usually caused by contact between metal surfaces, as this can lead to scratches.
Keep Talking About Extremes: Certainly highly low or moving temperatures is never a good option when talking about storage, it is advised to keep the temperature stable and within the range of 50–75°F.
Protect From Dust: This use of this equipment guarantees that dust does not accumulate on the tools over time and that the surfaces are not eroded or damaged due to dirt particles, so protective covers do help in that regard.
Following these practices, as mentioned above, will ensure that with preventative measures, tools stay in top condition forever and will not wear out or rust.
Top Recommended Water Pump Bearing Puller Kits for DIY Mechanics
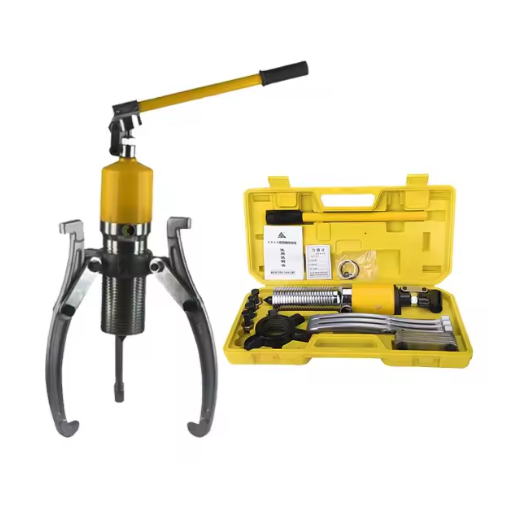

Budget-Friendly Options for Occasional Use
If you are searching for a water pump-bearing puller that is cheap and for occasional use, I would suggest looking for one that has the bare minimum features and is also a little cost-effective. An example of such a kit is the OEMTOOLS 27031 Water Pump Pulley Puller, their most recommended creation worldwide. It will suit people with light to moderate running or sewing machines used by other groups other than original manufacturers, making it appealing to DIYers. Within this kit, you get the following technical specifications as well:
Material Quality: their steel construction withstands occasional use without warping.
Compatibility: Designed to fit most domestic and imported vehicles, making it great for universal applications.
Ease of Use: a one-piece, compact build enables pressing off a wide range of pulleys that are pressed onto shafts to be removed.
Dimensions: adjustable components to guarantee proper engagement with various diameter pulleys.
If you want a more inexpensive but reliable set of components for added versatility, the Orion Motor Tech Pulley Puller Kit will work perfectly for you. In it, you shall experience:
Steel Construction: While it is built slightly weaker, some parts make it corrosion-resistant. This means you can expect reliable but occasional performance.
Broad Applicability: Not only is it easy to carry, but it is also easier to apply on multiple kinds of vehicles with additional pressed-on pulleys.
Portable Case: An advantage that comes with it is a substantial storage and organizational carrying case.
Both solutions are relevant to DIY mechanics who deal with rare jobs and are affordable. Remember to choose one based on your vehicle’s particular requirements and the kinds of pulleys that are likely to be used frequently with it.
Professional-Grade Pullers for Heavy-Duty Applications
Regarding heavy-pulling applications, quality pulley pullers should be in the arsenal as they are designed to offer strength and efficiency. I often suggest the OTC 4530 Puller Set for these scenarios. This specific puller is built for multiple and well-demanding applications, making it perfect for professional mechanics with large systems. Here’s why:
High Strength Construction: This puller is made of heat-treated alloy steel, which provides high torque capabilities and deformation housing properties.
Adjustable Jaws: The adjustable jaws are the talk of the day, as every size and shape gets a perfect grip while the tension is maintained at all times, ensuring its precautionary features.
Capacity and Compatibility: This set’s 10-ton pulling capacity makes it a must-have for large-scale projects, such as sprawling trucks or substantial industrial machines.
Precision Engineering: The highly accurate components are constructed to allow easy board maneuvers and minimize the chances of damage to any pulley surface.
Even the Snap-On CJ2002 Universal Puller is a favorite of some professionals. It has specialized attachments for increased versatility. Although it may be an expensive upfront investment in demanding applications, its functionality makes perfect sense in the long run.
Always evaluate the precise technical parameters and the kinds of pulleys used in your work to choose the best tool.
Versatile Kits with Multiple Adapters and Attachments
Multi-purpose mechanical tasks can be performed with the help of versatile kits with several adapters and attachments. These kits are developed to tackle the technical aspects of a particular pulley system and parts.
Pulling Capacity: Most versatile kits can pull off more than 10 tonnes with 5 tons supporting them, increasing the number of applications that can be used with them while keeping safety in hand.
Compatibility: Adapters are designed to fit various pulley sizes, from small automotive pulleys to larger industrial configurations.
Material Durability: Components are usually made with high-strength steel to prevent rapid wear and deformation when exposed to high-pressure usage.
Attachment Options: To enhance the kit’s utility, additional broad-scope attachments, such as the clamps and spreaders, are used for specialized procedures.
To briefly answer your query, if you require a toolset for heavy-duty operations more than once or for specific technical purposes, try to look for kits that can handle the pulling force needed. Most adapters can adjust to different pulley sizes, and the attachments would be right for your work. These parameters, too, justify the selection of the best and most effective tool available.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What do you mean by bearing puller pump, and what is its function?
A: A bearing puller pump is an apparatus used to extract bearings from water pumps. It consists of a central screw mechanism along with adjustable arms that are used to grip the target, which is to be pulled out. This medical apparatus is critical in automobile maintenance and servicing, especially when replacing water pump bearings.
Q: I would like to ask how I determine which bearing puller is the right size and style for my purposes.
A: To choose the right water pump bearing puller, you should first consider the size of those bearings and the type of water pump. You may try measuring the diameter of the bearing and checking the permits for that particular pump. You can also consider a puller type that adjusts teeth to accommodate different sizes. Pullers are also sold in sets with various arm and jaw lengths.
Q: What’s the difference between gear and bearing pullers?
A: Although both serve a similar purpose of extraction, their design works on different characteristics: A gear puller has been designed around the primary purpose of extracting gears, pulleys, and sprockets, while A bearing puller has been designed for the sole purpose of drawing out the bearing. Many bearing pullers have purposely shaped jaws to grasp behind the bearing race, giving them an advantage over water pump bearing removal.
Q: How do I use a water pump bearing puller to remove a bearing?
A: A water pump bearing puller is to be used first to ensure that the jaws are set to fit the bearing correctly. Once you have set the jaws behind the bearing, position the puller such that the jaws are gripping the bearing evenly. Using four fingers, tighten the central screw mechanism gradually, evenly pulling the bearing out. The main aim is to remove the bearing, but one must be careful about damaging the bearing housing. Some stubborn bearings might require the addition of penetrating oil as well as heat.
Q: Are there Water pump bearing pullers of different types?
A: Yes, there are Water pump bearing pullers of different types. These include manual screw-type pullers, hydraulic pullers for heavy-duty uses, a bearing puller for internal use for bearing pullers from blind holes, and slide hammer pullers. Each type has its advantages depending on the specific task to be done and the location of the bearing.
Q: What are the qualities of a bearing water pump while purchasing a bearing puller of a high standard?
A: When looking for a high-quality water pump bearing puller, consider the elderly belt clutch disc, jaw functionalized for adjustment and ease of use, and raised carbon elements. Evaluate the maximum ton force the puller can apply and whether a warranty is included. Reading the product reviews and watching the demonstration videos are also helpful.
Q: How can I clean and maintain a water pump to guarantee durability?
A: Every time the water pump bearing puller is utilized, it has to be cleaned so that debris or oil does not get into it. The living parts – the central screw mechanism – have to be greased to thwart rust formation and maintain functionality. The puller has to be kept in a non-humid space; otherwise, rust will form. As you use it repeatedly, be mindful of the wear and tear of the jaws and arms, and change them if your goal is to keep the efficiency and safety of the tool intact.
Q: Is there any other application for a water pump-bearing puller besides the water pump?
A: In addition to a water pump, a water pump bearing puller applies to other hydraulic devices such as alternators, steering pumps, and some transmission parts. However, it is best practice to double-check whether the bearing puller fits the job at hand, will not compromise any components, and will fit properly to the bearing.







