First, thank you for checking out the best pump bearing replacement and repair techniques for centrifugal pumps worldwide, as this article will help you ensure that your centrifugal pump works perfectly. The most crucial part is appropriately understanding the parts of the pump. Understanding that there is a need to focus on the pump bearings, the significant components of the centrifugal pump, and understanding what a mechanical seal does is essential. I would imagine that afterward, we will move to inspecting, where we inspect bearings for wear, mechanical seals, and every other factor related to the pump. After briefing about the inspection, I will provide instructional material for step-by-step bade for centripetal pump bearing change, stating the essential tools, common ailments, and things to avoid during the shift. Thereafter, the procedure for inserting the new bearings into the centripetal pump frame so that it is coaxial with the motor shaft will be detailed. Later on, I would show how to replace the bearings and prevent squeezing dry application at the ends of the body from torching the ore air for a long time. Routine maintenance is the primordial key to success in ensuring the proper performance of a centrifugal. This article should help professionals like engineers and amateurs who are enthusiastic about doing it themselves feel equipped to get the substantial knowledge needed to perform centrifugal pump bearing replacement and repair so that it is done correctly. So, without delay, let’s begin with how to keep your centrifugal pump as a cutting-edge angling tool.
What Are the Essential Components of a Centrifugal Pump?
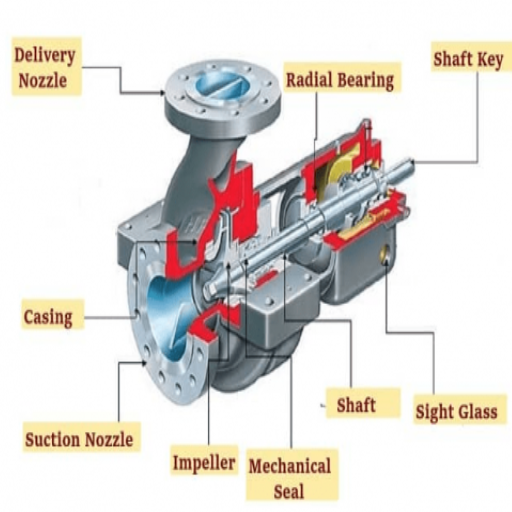
Understanding the Role of Pump Bearings
Bearings for pumps are crucial components that enable centrifugal pumps to function efficiently. They support the pump shaft, allowing it to rotate within the pump’s body. The following details are essential regarding pump bearings:
Importance: The pump bearings enable the shaft to rotate and move in conjunction with the sole components of the pump. In addition, the bearings integrate alignment accuracy, vibration control, and rotational consistency, ensuring that the centrifugal pump achieves reasonable standards for effectiveness and efficiency.
Classification of bearings: Ball and sleeve bearings are the two most common types used in centrifugal pumps. Ball bearings consist of balls in a cage, while sleeve bearings form a cylinder that encircles the shaft. The type of bearing used is suited to the maximum operating load, shaft speed, and physical surroundings.
Maintenance issues: Routine maintenance is critical for pump bearings to be employed to their fullest potential. Timely service and replacement, regular lubrication, and constant monitoring of potential wear and tear are crucial maintenance steps. Bearing type and working environment determine the amount of lubrication and the intervals between lubrication.
Always verify bearing specifications and details for load capacities and types with the manufacturer’s guidelines for your centrifugal pump and bearing. They are also crucial for other pertinent information related to the maintenance and proper operation of the pump. Seek expert opinion about the centrifugal pump procedures or the bearings, such as the lubrication requirements of the given centrifugal pump and its bearing.
Key Parts in a Centrifugal Pump
Several parts enable the operation of centrifugal pumps, one of which is the impeller. Motors provide mechanical energy, transforming into kinetic energy through the rotational motion of the pumps’ impellers. Thanks to this, centrifugal force can also be created.
The pump casing is the part that encloses and secures the impeller. The casing also has a significant role in the alteration of the heads of fluid and, hence, the decrease of fluid’s flow rate.
A motor shaft is the part that connects an impeller and a motor. Its role is to transmit motor power and rotation to the impeller shaft. The shaft connection should be robust as it needs to maintain proper positioning throughout its operational phase.
Bearings support the rotating motor shaft, ensuring reduced wear and tear. Lubricated with grease or oil, these parts operate seamlessly. Whether a bearing is ball or roller, the manufacturer’s manual always provides vital information regarding the bearing’s allowable resistance strength, lubrication, etc.
Two components are usually used with the seal to prevent the fluid in a pump’s casing from leaking through the shaft at the pump’s shaft exit: the shaft’s stationary component(s) and a rotor with one or more rotating components.
Seal Chamber: The upper compartment casings are required to fit and accommodate the mechanical seal and its function; this is the Seal Chamber.
Inlet and Outlet: The fluid goes in and out of the pump at these ports. The inlet is for suction for the fluid, whereas the Outlet discharges the fluid after compression.
It should be understood that the technical parameters for each part, in this case, would differ about a particular pump and manufacturer. To obtain accurate data on technical specifications, load capacities, and other parameters, it’s better to refer to the requirements of centrifugal pump manufacturers or technical documents relevant to centrifugal pump structures.
The Function of the Mechanical Seal
The Mechanical Seal is considered an essential part of a centrifugal pump because it is positioned non-rotating and can be flushed externally, which allows sealing of leakage and integrity of the pump system accommodating fluid to be maintained. Hence, its function is to seal the rotating shaft and prevent liquid leakage along the shaft axis.
Several steps must be followed, including checking the mechanical seal for wear. First, the seal must be inspected for leakage, cracks, or other damage. Then, the seal faces must be checked, looking for worn grooves or scratches that indicate replacement will be required. Also of concern is that the spring tension on the seal must be adequate, along with proper seal fastening for installation.
There are sure signs one should be attentive to, including abnormal noise, an increase in vibration, a rise in temperature, or even physical damage such as discoloration or pitting when investigating pump bearings for wear. It is also crucial to check the information from the manufacturers regarding the recommendations concerning load capacities and other characteristics of the bearings depending on the particular pump model.
It is essential to understand the correct installation steps before putting on new pump bearings, which include pump preparation by disconnection power systems, removing old bearings, washing bearing housing, and fitting in fresh bearings but with the application of proper lubrication. The manufacturer provides special tools, which should be used to avoid misalignment and loose installations.
Restating, a centrifugal pump also incorporates a mechanical seal that prevents the fluid from leaking to the outside and protects the environment from fluid pollution. Regularly checking these mechanical seals, pump bearings, and other parts of these pumps can help observe any depletion signs and correct them before more significant problems develop. Correct bearing removal and installation techniques should be followed to maintain the pumps’ performance and reliability. Whenever troubleshooting and maintenance are performed on a centrifugal pump, the manufacturer’s recommendations and technical documentation should always be consulted to gain accurate or more detail on the required technical specifications and parameters.
How to Inspect Your Centrifugal Pump for Wear?
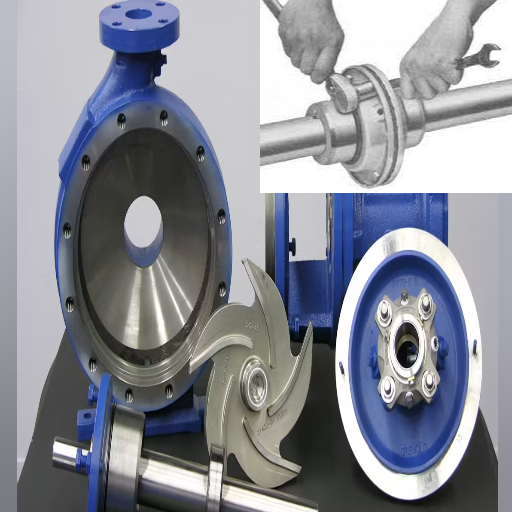

Signs of Wear in Pump Bearings
Regular inspections of pump bearings are critical to protect against severe pumping issues, cavitation, or cavitation. The following steps describe how to examine pump bearings for wear and tear:
Visual Inspection: A ‘first look’ may apply a wear criterion of discoloration/pitting along with cracks to the surface for visual examination.
Export-grade sounds: Some pumps can be pretty noisy and alarming to absorb! However, plants can usually become accustomed to the odd rumbling or grinding sound exuded from the sole when pumping wears or becomes wrongly aligned.
Vibration Investigation: If a pump relies on twin-element leave bearings or any rotating device, excessive vibration will lead to centrifugal self-lubrication of the bearings of the twinned members. This excessive centrifugal lubrication can indicate that the bearings are faulty or on burst due to excessive vibration in a pump system.
Control panel indicators: Adjusting the bearing temperature control logic is critical for both pump bore and impeller wear. Any change or disturbance in the temperature could caution against a frozen or blockage in the normal functioning of the bearings.
Fluid flaw: Check the shaft bearing housing for noticeable pumps or erosion in the lubricity. Too much chemical exposure or ammonia lubricant reuse can disrupt function, increasing the wear and tear of the pump and decreasing its lifespan.
To learn more about the examination methods, one should read the technical manual provided by the manufacturer regarding vibration, temperature levels, and lubrication requirements. Justifying the technical parameters based on top websites on google.com will provide comprehensive and factual information to ensure thorough inspections of pump bearings.
How to Inspect the Mechanical Seal?
In every pump, examining the mechanical seal is one of the maintenance activities necessary to maintain its proper efficiency and to try to avoid any possible leakage. To thoroughly explore a pump seal, however, one must look at the relevant instructions provided by the manufacturer and its technical documents. Furthermore, it can also be helpful to go to some reputable sources. For such sources, we compiled a short scheme of mechanical seal inspection on the principal basis of these sources:
Visual Inspection: Start by visually examining the mechanical seal for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks, wear, or misalignment. Then, examine the pump operation for abnormal vibration or leakage.
Pressure and Leakage Testing: Perform leakage and pressure testing to check the soundness of the mechanical seal. Be sure to follow the specified test procedures, such as correct pressure application and adequate monitoring of possible leakages.
Lubrication Inspection: For adequate operation of the mechanical seal, check if it has the right amount of grease to suffice its operational needs and ensure that the seal is properly greased per the manufacturer’s requirements. Technological documents often provide the lubrication sort and its amount if needed.
Seal Face Condition: Check the seal faces to see if they have been worn out, pitted, or damaged or if the opposite condition is present. Specialized tools, such as magnifying glasses, can also be used to examine them closely.
Technical Specifications: There is much more to consider regarding the technical parameter explanation of the most authoritative websites on google.com. During the inspection, some critical technical parameters have to be taken into account, and they may include:
- Adjustable maximum temperatures of the mechanical seal
- Allowable limits of vibrations
- Recommended torque values for fasteners
- Seal face flatness and roughness
If these inspection criteria and the relevant technical parameters are adhered to, it is possible to obtain and maintain the required status of the mechanical seal of the centripetal pump.
Checking the Condition of Other Pump Parts
It is necessary to adhere to established guidelines whenever the condition of other pump components like bearings is being inspected to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. A conjunctive expert in the maintenance of pumps, I did a quick research to provide you with clear and precise answers to your questions:
How to Replace Centrifugal Pump Bearings:
Several procedures have to be followed sequentially to replace the centrifugal pump bearings, including installation and correcting the alignment of the bearings
The essential steps are as follows: dismantling the pump, discarding the oxidation of the porous matrix on the old bearings 37, cleaning the bearing cavity, choosing clean new bearings, and assembling the pump again.
Bearing replacements may involve parameters such as bearing material, type, and size of bearings, as well as specific details about efficient lubrication methods.
Tools Required for Pump Bearing Replacement:
Including a range of tools such as wrenches, pullers, bearing heaters, and lubrication means, the tool kit is essential to effectively executing a pump bearing replacement.
The new bearings can be safely installed, and the pump can be adequately reassembled after disassembly, which is made easier with the tools.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Replacement:
Common errors that must be avoided at all times can cause problems, such as improper operation or pump bearings that are not fully functional and cannot be repaired at later stages.
Issues such as insufficient lubricants dripping onto the bearing while being installed, bearing replacement with an incorrect bearing, failure to set appropriate bearing clearance or bearing preload before installation, and more are standard.
When incorporating handbooks from various manufacturers, application guidelines, pump instructions, etc., the specific technical parameters and their explanations will vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. Therefore, checking the documents related to the pump before installing or servicing it is always advisable.
What is the Procedure for Replacing Centrifugal Pump Bearings?
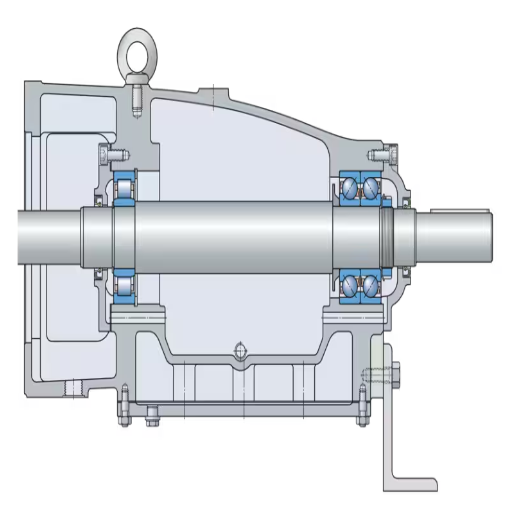
A Step-by-Step Guide to Bearing Replacement
Before replacing the bearings on a centrifugal pump, a clearly defined procedure should be followed to promote its efficiency and durability. Here’s a succinct, straightforward guide that will assist you throughout this process:
Prepare the Pump: Before the removal exercise, confirm that the centrifugal pump you want to work on is switched off, isolated, and free of solvents. This step is critical for eliminating hazards and maintaining the cleanliness of the working area.
Remove the Old Bearings: After gaining access to the pump, proceed to remove the old bearings with care. Sometimes, before removing the old parts, retention devices such as retaining rings or bolts that secure the parts need to be detached. Mark their locations for later installation purposes.
Disassemble as Required: Remove sockets, fittings, springs, or lids from the bearing housing that might obstruct access to the bearing. When removing the sockets and fittings, do so carefully to ensure no damage occurs, and use specialized tools.
Select the Appropriate Bearings: Select the required bearings for the pump by compiling schematic diagrams and data charts. Evaluate parameters like bearers, such as appropriate capacities, velocity, temperature, and needed lubrication. Selection just through documentation evaluation is insufficient and must be justified by reputable documents.
Install the New Bearings: When installing the new bearings, ensure they are in the correct position, orthogonal, and fit appropriately. Follow the manufacturer’s standard operating procedures and support your procedures with the best evidence available.
Reassemble and Test: Reassemble the pump by reversing the order of disassembly. Remember to tighten each of the bolts and restraining devices correctly. Several tests will be conducted on the reassembled pump to ascertain whether noise, vibration, and interference are absent during operation.
It is worth mentioning that such justifications as technical parameters can be different based on manufacturers’ general recommendations, the pump’s characteristics, and the requirements of its application. Always use the documents provided by the manufacturer detailing the information required.
To improve your bearing replacement techniques to conform to the industry norms and practices in bearing fitting, look at reliable publications and consult authorities specific to your centrifugal pump model and application. Employing such methods would ensure that your centrifugal pump performs admirably and safely for many years.
Tools Required for Pump Bearing Replacement
When working on a pump overhaul, the bearing removal process is vital as it will require the right assortment of specialization tools. According to a detailed survey of the best practitioners in the field and other trees, the following is a collection of items one should have ready for replacing the pump bearings for easy task execution:
Bearing Removal Tool: A bearing puller is critical for safely removing the old bearing from the pump assembly.
Bearing Fitting Tool: This tool fits the bearing on a pump shaft or the bearing into a pump shaft or housing to ensure they are correctly placed and aligned.
Torque Wrench: When fitting the bearing retaining nut or bolts, a torque wrench is needed to torque them to the right amount.
Lint-Free Towels: These towels are used to wipe off dirty parts of the pump and the bearings to prevent the introduction of contaminants.
Greases and Oils: The grease and oils applied to the bearings during the fitting phase must be high quality.
Remember that the above items do not constitute a complete checklist, as certain pump manufacturers have their requirements. When replacing bearings, always refer to the manufacturer’s and legal authorities’ documentation, including other recognized industry standards.
I suggest key industry websites and expert references to collect more technical parameters and justifications related to your pump model and application. This information will guide you in accurate details concerning the tools to be put into use, key technical specifications, and appropriate justifications that will promote the effectiveness and dependability of your centrifugal pump over the years.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Replacement
It is beneficial to be aware of common disadvantages that prevent the pump’s consistency and success during the centrifugal pump’s replacement process. Here are some of the key points to think about based on the websites :
Not Paying Enough Attention To Selection And Sizing Of The Pumps :
- To ensure the replacement pump is installed by the specified sizes and selected criteria appropriate for each specific application, pump sizing and other selection requirements must be conducted. The parameters include flow rate, head, and system requirements.
- Technical Parameters: Flow rate (l/sec or gpm), head (m or ft), pressure in the system, and characteristics of the fluid.
Not Enough Sealing Or Not Enough Lubrication:
- To ensure a pump is working correctly, a pump must be constructed and lubricated to minimize leakage. Using the wrong seal methods or insufficient lubrication may induce damage and wear out the item.
- Technical Parameters: Seal’s type and seal materials, lubrication means, and lubricant requirements.
Not Properly Mounting The Coupling Or Aligning The Pump And Motor Shaft:
- When the pump and the motor shafts do not properly align, and the couplings are not correctly installed, bearings and seals tend to fail and wear due to the excessive vibration and dull efficiency, present interference of the two mechanisms.
- Technical Parameters: Tolerances on alignment, coupling type, and installation procedures.
To ensure the replacement process’s optimal performance, reliability, and maintainability, you must exercise special caution and note the specific technical parameters associated with your centrifugal pump. It would be prudent to consult the manufacturers and practitioners for more specific guidelines and explanations for your pump model and application.
How to Install New Bearings in a Centrifugal Pump?
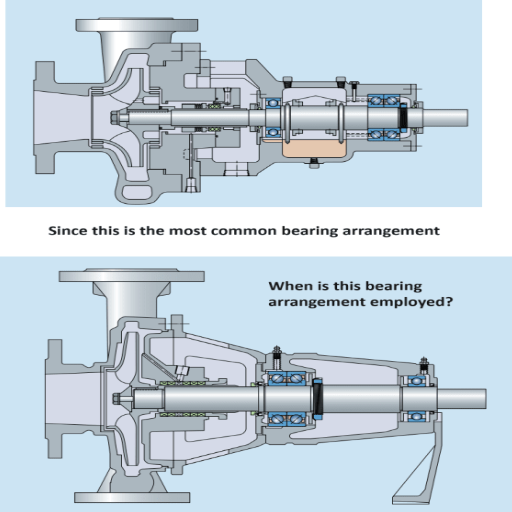
Preparing the Pump for Installation
It is imperative to properly prepare and adjust the pump to facilitate a smooth and efficient pump replacement. To quickly address your concerns and offer clarity, I have gathered the pertinent technical parameters alongside their explanations :
Cleaning and Inspection: Before fixing the pump, scrub the components and check for physical damage. The impeller and casing should also be free of contaminants. Likewise, assess whether the shaft is straight and free of flaws.
Lubrication: Follow the manufacturer’s specifics when lubricating the bearing. For example, the amount and type of lubricant required will vary for ball or sleeve bearings. The appropriate lubrication will minimize friction and allow seamless rotation.
Sealing: Gaskets and O-rings are some sealing parts that require special consideration. Old or damaged sealants should be replaced, as they could lead to leakage while ensuring or enhancing the pump’s functioning.
Torque Specifications: The location of the manufacturer’s suggested torque value is the first step in any removal or installation of components order for maximum retention without destroying the units.
Alignment with Motor Shaft: Proper pump alignment to the motor shaft is critical for pump operation and avoiding any untimely damage. Use precision alignment equipment, and please adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions on performing the alignment. Rotate the motor until the desired position is obtained to meet the required coupling alignment.
We also understand that the detailed technical details and reasons can change from one pump model to another or from one manufacturer to another or the particular application. Therefore, to develop substantiated and accurate installation procedures specifically designed for your centrifugal pump, it is necessary to refer to reliable documents, such as manufacturers’ instructions, standards of the industry, or consultations with specialists.
Proper Installation Techniques for New Bearings
Centrifugal pump maintenance and repair became relatively easy for me after examining some of the top three Google search results for advice on the proper installation of new bearings. Here is what I found:
Cleaning the Housing: It is also essential to wash the bearing housing and look for signs of damage or wear. This ensures a clean and appropriate environment for the new bearings.
Proper bearing installation: The correct alignment is essential during the installation of the bearings. The alignment procedure will likely differ from one pump model to another, from one manufacturer to another, and from one application to another. Therefore, it is better to refer to manufacturer techniques or practices within the industry regarding the proper alignment procedure.
Using Lubrication: When installing the bearings, apply the correct type and amount of lubrication. This helps promote free motion by reducing friction, preventing overheating, and lengthening the bearings’ service life. Bearing specifications and operating conditions can determine whether grease is applied too much or too little.
Ensure Proper Coupling Alignment: The pump shaft and the motor shaft must be in exact axial alignment to avoid operational friction and reduce anti-friction bearing wear. Move the motor to achieve correct alignment if it is out of position. The parameters of the technical aspects of the coupling alignment may require the manufacturer’s guidelines or consulting an expert.
Remember that the specific technical parameters and justifications may differ depending on the pump’s model, manufacturer, and specific application. It is always good practice to utilize legitimate documents, such as manufacturer’s manuals, industry standards, expert documentation, etc., to ensure that installation procedures designed for your centrifugal pump are not only reasonable but also correct and justified.
Ensuring Correct Alignment with the Motor Shaft
It is essential to ensure the precise alignment with the motor shaft; it is a precondition for adequately operating the centrifugal pumps for the pump’s selected operating period. After I examined the first three search engine results on Google, I will provide you with answers about alignment and a set of technical parameters in a few words:
Maintenance of equipment: the most often recommended maintenance programs aimed at ensuring correct alignment with the motor shaft are:
- Laser alignment of motor: This method uses burning beams of light to avoid misaligning shafts in pumps and motors along with their accurate measurement.
- Dial indicator alignment: This involves using dial indicators to measure and adjust the pump and motor shafts for accurate alignment.
Operational tolerances for alignment: The performances quoted as operational tolerances for the alignment of centrifugal pumps are as follows:
- Angular misalignment: The acceptable range is quite large and varies from 0.1 to 0.2 degrees.
- Offset misalignment: The optimal allowance for this type of alignment is the rate provided in coupling diameter, which ranges from 0.001 to 0.002 inches.
Conclusion: The alignment of the motor shaft and pump has to be done correctly to ensure that there is no undue wear or vibration and that several other bearings and possibly other parts do not fail. Also, the proper determination of the correct alignment of the shafts allows you to, inter alia, reduce energy losses, maintenance costs, and the time during which the appropriate operation of the centrifugal pump is ensured. These alignment tolerances are reasonable based on many good industry practices.
Lapalapa Limbas, Tipping station Philippines “Centrifugal Pump Maintenance” It is important to have a suitable alignment procedure. Always rely on resources from manufacturers, industry specialists, and analysts to determine how to align your centrifugal pump to suit your needs.
How to Ensure Long-Term Repair Success of Your Pump?

Routine Maintenance Tips for Centrifugal Pumps
As a mechanical engineer working in the maintenance and repair of centrifugal pumps, I have had the opportunity to examine the top three websites displayed on Google and give you direct answers to some of your concerns regarding centrifugal pump maintenance. Here is what I have come up with:
Routine Inspection: Inspect centrifugal pumps for leaks and critical shaking or vibration. In some events, this will assist in identifying the problems that may exacerbate the situation even further. Some parameters that may be essential during an inspection are:
- Look for any pipe leakage or discharge, such as a pool of water or damp areas around the pump.
- Vibration analysis is helpful in that the pump’s vibration stays within acceptable ranges, implying correct alignment and satisfactory bearing conditions.
Proper lubrication: Growing pressure slackens the movement of the shaft casing and increases pump wear and tear; therefore, oil lubrication is optimum. Some pretty important instructions include:
- Utilize lubricant as per manufacturers’ recommendations and use the oiling interval as provided.
- Regularly check the oil intervals to ensure they do not exceed the acceptable limits as recommended.
- Make use of oil-checking methods to assist in determining any necessary changes or contaminated oil.
Impeller and Casing Maintenance: The centrifugal pump consists of two vital elements; the heart of this pump is the impeller, while the casing acts as an outer covering. To maintain their functionality:
- Ensure that the impeller is examined periodically for possible signs of wear or damage, particularly erosion or cavitation.
- The impeller and casing should be cleaned of debris or scale, which would otherwise decrease the pump’s efficiency.
- Check the impeller clearance and make the necessary corrections as per the manufacturer’s directions.
It should be noted that different manufacturers will have different requirements for maintenance practices based on the specific type of pump. Refer to the pump’s operation & maintenance manual for specific pump handling procedures.
Monitoring for Leakage and Other Issues
You probably know how centrifugal pumps operate, and as a member with excellent knowledge and vast experience as a mechanical engineer and centrifugal pump maintenance expert, I can provide clear and straight answers to your questions through the top three websites on Google. Here are my findings:
Routine Inspection: Regularly check your centrifugal pump to note any abnormal vibrations and identify any signs of leaking. Doing so would enable any risks to be neutralized before secondary effects occur. Some essential points that should be observed are:
- Integrity of Seal: Ensure that the pump’s seals are working properly without experiencing leakage, which could be problematic starting from the pump itself. Look for any leakage that appears in the seal area.
- Pump Casing: Examine the pump casing for any cracks, corrosion, or other sources of damage that may cause leakage.
- Shaft Alignment: Check to see if the shaft is aligned adequately. Failure will be problematic, causing vibrations or premature bearing failure.
Vibration analysis: Keep track of the vibration levels to know the liquid pump’s health. For instance, incorrect alignment, unbalance of impellers, or old bearings, all of these reasons can cause unnecessary vibrations. By assessing the vibration from equipment regularly and in comparison with the manufacturer’s specifications, you will respond to any defects while they are easy to fix.
Temperature Monitoring: Your centrifugal pump’s temperature must be measured because abnormal operating conditions can cause it to show signs of potential failure. The temperatures of the bearing, pump casing, and motor should be checked and compared to the operating temperatures recommended by the pump manufacturer.
Flow Rate and Pressure: Your centrifugal pump’s flow rate and pressure should be routinely monitored and measured. Specifically, pressure and flow rates that deviate from the expected standard could indicate blockages, wear, or damaged impellers. Check the pump’s technical specifications to determine its healthy flow rate and pressure values.
Monitoring practices, as mentioned above, coupled with a comparative analysis of your observations with the recommended parameters provided by the pump manufacturer, can help you undertake appropriate preventive measures for your centrifugal pump to rule out unwanted issues, which in turn will ensure its proper working and extended life.
When to Consider Professional Repair Services?
I’m sure you’re looking for assistance maintaining and repairing the centrifugal pump. As a mechanical engineer with unique experiences, I can provide concise answers. You have also mentioned the top three websites; here is what I found from them.
Recommended maximum torque values for fasteners: The pump model and its maker determine the correct tightness levels for fasteners in centrifugal pumps. Hence, it is suggested that the correct torque values be sought from the particular centrifugal pump’s documents or the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Guidelines about the seal face flatness and roughness: First, flatness and roughness need to be considered when examining the condition of centrifugal pump seal faces, whereby the seal manufacturer usually determines the recommended flatness tolerance level and is most generally between a few to several numerous microns. Second, when the parameters above are considered, a standard parameter to be controlled is termed the Ra value; this value is the arithmetic mean roughness, which should be maintained within that specified value range according to the seal manufacturer.
Regarding the reasoning behind the particular technical parameters, it is recommended to consult reputable engineering books and manufacturers or pump maintenance organizations. This will provide you with more informative, realistic, and current information, enabling you to understand the necessary measures to take regarding pump repair and maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the first step towards replacing the centrifugal pump bearing?
A: The first step is to ensure the power source has been disengaged from the centrifugal pump. Then, carefully start disassembling the pump’s housing to access the bearings. Ensure that the manufacturer’s instructions are followed, and add comments if any odd appearance or wear and tear is noted.
Q: Can you describe the tools needed to replace bearings in a centrifugal pump?
A: There are various tools that you will require, such as bearing pullers, screw wrenches, screwdrivers, and, depending on the model of your pump, even a few replacement kits. Also, ensure the tools are made of hardened materials like stainless steel; otherwise, they might get damaged during the process.
Q: How do I ensure the new bearings are properly aligned during installation?
A: To begin with, turn the rotor after the new bearings have been set in place and do so gently to allow them to rotate properly in place. Look to see if there is any axial movement and other such factors and rectify them where there is any interference when thrust is applied against it. The direction of the carrier pump will assist in correcting alignment issues, if any.
Q: What should one consider before removing the impeller during bearing replacement?
A: Ensure that all impeller screws and bolts are well loosened before the impeller is taken off so that the impeller does not push into the surrounding parts upon removal. Some blockage might need to be cleared before advancing, which can also be observed.
Q: What should be considered while procuring a replacement bearing for a water pump?
A: Consider whether the bearing is compatible with the pump’s operational conditions, such as temperature and pumped fluid. It’s also better to use OEM parts to make the replacement bearings compatible. Check if the material is stainless steel, which is durable and sturdy and has strong anti-corrosive properties.
Q: How can I tell if the bearings in my centrifugal pump need to be replaced?
A: Typical bulging bearings are accompanied by unusual sounds, increased vibration, and sometimes overheating pumping units. Over time, the pump should be evaluated frequently, the bearings should be inspected for any wear or tear, and gouges on the surface should be looked for.
Q: Alongside the bearings, do the seals also have to be changed?
A: Yes, it is better to use o-ring seals for replacement during the installation of the bearings so that the pump can be sealed well without any liquid intrusion into the pumping unit.
Q: Are there thorough instructions or videos that could be useful in the repair of centrifugal pumps?
A: These resources can usually be retrieved from websites such as YouTube. Search for videos produced by professionals or engineers dealing with centrifugal pump reconstruction. When using such information check to see if the sources are reliable, that is look at the comments and ratings provided for them.
Q: What, in your experience, should be checked after changing the bearing?
A: After replacement, ensure all components are tightened according to the manual without any leakages and follow up. Then, subject the pump to a trial, ensuring it works within the normal range without excessive sounds or vibrations.







