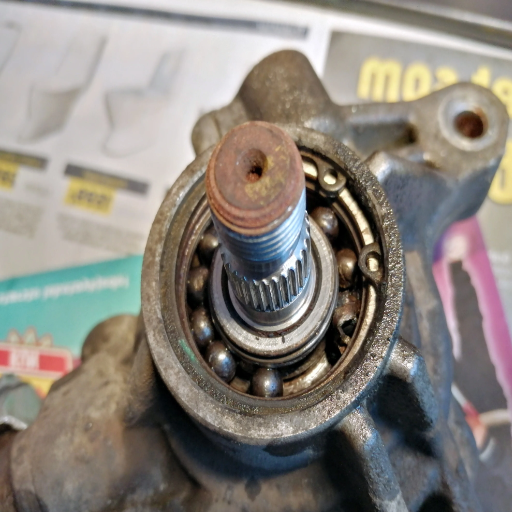
In most instances, replacing the bearing in a power steering pump may appear more straightforward. However, if a person carefully follows directions and understands the tools required to carry out the task, replacing the steering pump should be easy and hassle-free. This article will provide a step-by-step replacement valuable guide to mechanics, particularly DIY people. From the functions the steering pump plays in the proper functioning of the vehicle to determining if a bearing is bad, we will cover each critical step in detail. Doing so will give you the relevant information and skills to make dealing with this common problem easy. Hang on and be ready as you witness the smoothest repair process.
What is a Power Steering Pump Bearing?

Understanding the Pump Bearing Functionality
The bearing of the power steering pump is integral to the proper functioning of the vehicle’s power steering system. It does so by allowing the rotation of the pump shaft so that the necessary hydraulic pressure for the easy turning of the steering is developed. Such bearings are manufactured to accommodate high rotation speeds with considerable radial and axial loads and are, therefore, reliable and durable.
Bearing type: Ball or roller bearings are usually incorporated because they rotate faster and handle heavy loads.
Load capacity: Designed for axial and radial loads, Axis and Bearing pointing forces are typically portrayed in Newton (s).
Material: Constructed usually out of hardened steel and other steel-metal combinations to withstand wear, corrosion, and high stresses.
Rotational Speed: These bearings are rated for over 1000 RPM and up to 4000 RPM.
Lubrication: Sealed bearings are greased before installation to reduce friction and increase their life expectancy by around 100,000 hours. Open ferrules are often required to be serviced annually.
Steering components require regular service. If service is neglected and the power steering pump bearing mounts age, this tends to result in high stress in the steering assembly. This may lead to high power assist failure, wailing or squealing sounds, and rotational grinding. If not addressed, internal rotation slippage may cause catastrophic failure during the power steering pump bearing operation.
Common Symptoms of a Failing Bearing
Unusual Noises: Poorly maintained bearings emit peculiar soundings like whines, groans, or rumbles during the vehicle’s operation. These noises denote high frictional contact or damage to the bearing’s internal components.
Vibration or Rough Operation: A damaged bearing can cause noticeable vibration or uneven motion. This is more pronounced when high speed is attained or when the steering wheel is turned.
Excessive Play Or Looseness: There is an increased amount of play or looseness of all bearings in the affected assembly that are worn out and compromises system accuracy and performance.
Overheating: Friction causes most bearings to decrease their yield. For steering pump bearings, this can cause a dramatic increase in temperature, around 80 to 100 degrees Celsius, which is usually above their functional temperatures.
Visual Damage: Replace such items when physical evidence of wear on bearing surfaces, such as cracks, pitting, or corrosion, has been observed. These signs indicate the bearing’s failure.
Early detection of such issues enables the prevention of further damage to adjacent components and the integrity of the whole system. Correct diagnostic equipment for technical testing is needed, such as a stethoscope for noise checks or an infrared thermometer for overheating.
Why Bearing Replacement is Crucial
Rolling bearing replacement is necessary since it affects the mechanical systems’ operating efficiency and life expectancy. Life-worn or broken bearings create more friction, heat, and vibration, detrimental to the system’s performance. In most cases, I have seen maintenance of this type being ignored, resulting in unplanned downtime, expensive repair works, and safety risks.
Some important operating characteristics that I examine in the course of bearing replacement are as follows:
Operating Temperature – When operating in an oven, it is easy to understand that their temperature is appropriate in the range of 120oF to 180oF (49oC to o82). If anything outside this range temperature, there is excessive heating or no oil.
Vibration Levels – Available through vibration analysis tools, there is a limit outside which a vibration level is assumed to cause a fault, which can be due to misalignment, wear, or imbalance – for instance, ISO 10816.
Lubrication Condition—Quality lubricants are formulated to withstand high temperatures without contaminating them. If the lubrication has deteriorated or become contaminated, it affects the bearing’s operating life.
Noise and Audible Irregularities—Abnormal noise in mechanical assemblies, such as grinding or clicking sounds, can indicate the internal breakdown of the rolling bearing.
Considering these parameters promptly and providing clear argumentation for the necessity of replacement, I can maintain reliability, safety,y and low costs of the mechanical system throughout its operation.
Where to Store the Necessary Parts and Tools?

Essential Tools for Replacement
In parallel with including additional components and procedures for the bearing replacement to increase its intensity, I also ensure that the following tools are available and maintained adequately.
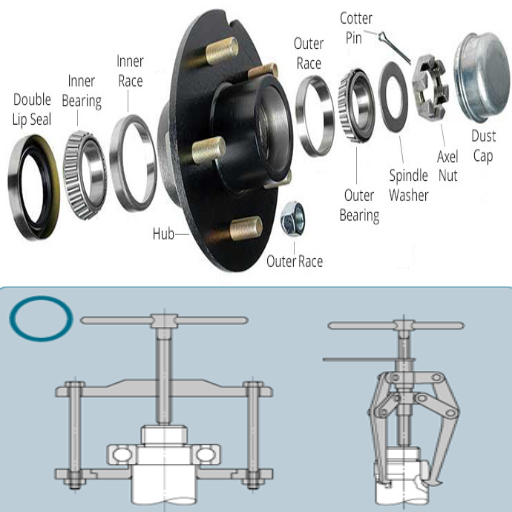
Bearing Puller/ Extra Services or Fitting: This tool must be part of a bearing replacement as it helps the splitter remove deteriorated bearings without damaging the making parts.
Torque Wrench: All bolts and fittings must be included to guarantee enough torque if it exceeds or is lower than the recommended standards.
Seal Puller and Installer: They help loosen and place the seals properly, which is necessary for the bearing bracket so that it does not become rot and filthy.
Micrometer and Dial Gauge: These tools also enable me to optimize shaft diameter and bearing clearance patterns to ensure they adhere to manufacturers’ requirements.
Lubrication Tools: Engineering instructions regarding the amount of grease and oil used are critical in the process, and these elements serve precisely that purpose.
Cleaning Supplies: Also, make sure that the areas and parts are spotless so that no crossing contamination happens and lint removal is done by scrubbing.
Bearing installation with a set of parameters is more of a practice than science or knowledge, so I could simply “replace” a bearing. On the other hand, bearings are critical to system performance, reliability, and longevity.
Finding the Right Bearing and Seal Kit
To locate the appropriate bearing and seal kit, I consider many critical characteristics that would provide compatibility and improvement for the application. The first step is to decide what bearing is necessary depending on the load direction, such as whether radial, axial, combined ball bearings, roller bearings, or thrust bearings are needed. The next step is to ascertain the dimensions of the bearing, such as the inner diameter ID, outer diameter OD, and width so that it fits the housing and shaft in question.
The next consideration is the load capacity and the speed rating of the bearing to ensure that the bearing in question will work in the intended locations without overloading the bearing. The intended operating conditions such as temperature range, types of lubricants to be used and degree of environmental exposure (dust, moisture or chemicals) are essential in ensuring that the right seals in terms of protection against contaminants and risk of exposure are selected.
All in all, the most vital aspect that I take into consideration is the manner of sealing, whether it is contact, non-contact, or labyrinth seals; therefore, I ensure the seal kit I choose will not only be compatible but will also be able to withstand the type of bearing in question. After considering all these factors, I can confidently pick the most appropriate fit bearing and seal kit suitable for the requirements of the mechanical system.
How to Use an App for Easy Bearing Replacement?
Top Apps to Assist with Power Steering Maintenance‘’
In this segment, I pay particular attention to those applications that affect the maintenance of the power steering system. I have identified a few quality applications that require reasonable technical parameters on the subject. Here’s a list of the top tools I often use:
Hydraulic Calculator: This app guides parameters such as pressure, flow rate, and power in hydropneumatic power steering systems. I mainly rely on the app’s ability to assist with calculations of fluid viscosity and pump displacement.
TorqueSpec: About the nuts and bolts of the steering system, I thoroughly appreciate the importance of ensuring correct torque specifications that pertain to such nuts and bolts. As a ‘hands-on’ person, stop-go works in practice since the application of TorqueSpec protects overshooting the set torque for the components.
Bearing Health Dashboard: This application is crucial for identifying the condition of bearings in power steering pumps. To prevent failure, the app monitors specific parameters, including vibration temperature levels and lubrication.
This chapter is informative, offers easy applications, and saves time and reduces the chances of manual error. These factors enable me to comfortably carry out power steering maintenance without any worries about changes in technical parameters.
Step-by-Step Guide: App for Shaft and Pulley Alignment
Using an application to align pulleys and shafts helps save time while achieving accuracy, which is paramount to ensuring machinery efficiency. These applications can be claimed to enhance the alignment process by incorporating laser alignment, tracking in real time, and visualizing the results on the spot. In addition to reducing labor work, they also reduce the probability of a person’s error and assist in maintaining drive efficiency by obtaining perfect alignment.
To start, you must download an app that supports it on a device such as a smartphone or a tablet. Use the sensors that are usually packaged together with the app and position them on the shaft and pulleys depending on the different screens of the app. Ensure the sensors are affixed tightly and properly zeroed to fix a reference point, then proceed to commence calibration. The output of the sensors regarding misalignment value is indicated in figures or pictures on the screen, which guides you on adjustments. Some applications even suggest the appropriate adjustments to speed up the process.
In most apps, alignment tolerances (generally tolerances of a few hundredths of a millimeter) or angle deviations are prominently displayed. The advice is to” comply with those rules and verify the positioning before switching the equipment on.” The advice also includes ensuring that the sensors are mounted on a stable surface and monitoring the measurement again after adjustment to account for shifts that may occur during the tightening process. Thus, maintenance costs will be reduced with even more competent use of these apps.
How can the power steering pump bearing be replaced efficiently?
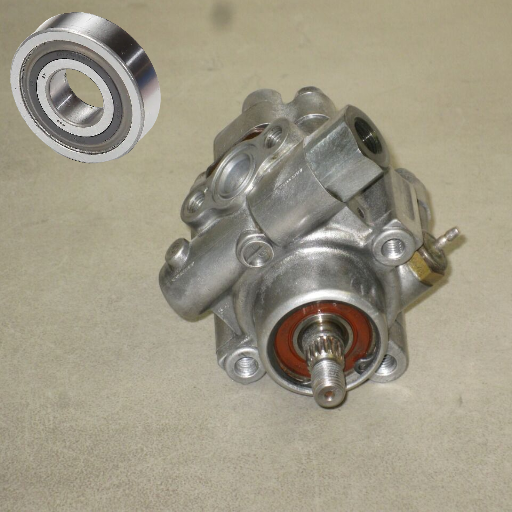

Step-by-Step Replacement Process
Preparation and Safety Measures: I check that the car is adequately secured, the engine is turned off, and all tools, such as socket wrenches, bearing pullers, and even a replacement bearing, are at hand. Protective gear, such as gloves and eyewear, is also worn to avoid injuries.
Removing the Power Steering Pump: The power steering pump is disconnected by unscrewing and unbolting the bolts connecting it to the mounting bracket. First, tension from the do belt is released on the pump, and all hoses connected to the pump are then loosened off to avoid the spillage of the fluid.
Extracting the Old Bearing: I use the bearing puller to remove the other side of the worn-out bearing from the pump shaft. It is worth taking precautions here because there is a chance of damage to the shaft. Some lubricant over there may assist somewhat in bearing removal.
Inspecting Related Components: Immediately before the bearing installation, the pump shaft, the housing, and some nearby parts are checked for wear or deformation. This ensures all parts have an acceptable condition to carry the new bearing.
Installing the New Bearing: I carefully place the new bearing onto the pump shaft, aligning it precisely. I carefully and evenly press the bearing into place with a press tool or mallet to avoid any dislocation.
Reassembling the Pump and Testing: Once the new bearing is held, I put back the power steering pump into a position where I disconnected it, attach hoses, and ensure the belt is at the proper tension. To complete the process, I re-inject fluid into the reservoir and observe for leaks.
In this way, if all the following steps are observed and the parameters set, I can replace the power steering pump bearing efficiently, and there is a guarantee that the mechanism will work afterward.
Handling the Power Steering Pump Pulley
The power steering pump pulley must be well maintained and protected from undue wear if the system is to be functional. Proper installation and alignment become paramount since the pulley is key in transmitting power from the engine to the pump. The problem, if this is not observed, is that the belt may lose its alignment, wear unevenly, or the system might fail; there is a need for [proper protocols and tools.
While removing the pulley, Always apply a pulley puller tool to it so that the pulley or the pump shaft is not damaged. Apply some pressure on the tool after ensuring the fasteners are loosened, and the tool is tightly secured. On the contrary, Installing a pulley requires correct orientation. Use the press tool or an installer kit to apply the pulley onto the shaft until it is level with the face of the pump. To prevent the tension from being too much or the belt from slipping out of place, verify the accuracy of the alignment with the drive belt. To ensure it is not too loose or tight, apply the manufacturer’s 18 to 22-foot-lbs torque values.
Common concerns include misaligned pulleys, warped components, or stripped threads during the assembly. Before reinstallation, you must check the belt and pulley for any damage. In addition, checking whether the installation has gone well by turning the item post-installation can reveal minor positioning differences. Following these recommendations will allow you to extend the power steering system’s service life and efficiency.
Testing the New Bearing Regarding Hum and Operational Aspects
Once the new bearing is fitted, noise and performance testing are necessary to ensure operational effectiveness. In many cases, noise is cited as a marker of threat—lack of lubrication, mounting defects, or misalignment, which causes weak bearing resources. As expected, performance tests aim to assess the working characteristics of the bearing mounted in the structure under load, where such efficiency could never reduce the machinery’s effectiveness.
To ascertain that the various components of the machine are working correctly, one should begin by operating the equipment at lower ranges to check for any unusual noises like whining, grinding, or clicking sounds. When in perfect working order, bearings should operate without any noise, and oil or grease inside them should be sloshing around freely. Check whether the temperature level is on the rise while increasing the speed. Although the temperature of a typical bearing should be around 70°C (158°F), it is subject to change with different specifications. Vibration analysis tools can also be employed to monitor vibrations caused by eccentricity or unbalance of the bearings, for which the general limit of vibration is considered below 4.5mm/s in RMS (Root Mean Square).
To avert such chances, be sure that the required lubricant amount meets the minimum recommended levels and that the proper bearing lubricant is used in the machine. Next, look for any slack in the shaft and housing, as the presence of slack would lead to instability. Making a habit of going back and rechecking at an early stage of use would be helpful to detect problems before they bane on and combine intercession. After doing all these, you can determine whether the newly installed bearing runs efficiently and under its operational limits with minimal noise.
How to Prevent Future Power Steering Pump Issues?

Essential Procedures for Pump Bearings Maintenance
It is essential to understand that regular maintenance of bearings will result in longer bearing life and improved pump efficiency. Pump failure can result from a lack of bearing oversight, which will increase friction and heat. The solution for that is to set up a maintenance schedule and stick to it so that it will apply to the type of bearing and the operating conditions of bearings.
Bearings must be lubricated at intervals prescribed by bearing manufacturers, usually 500 to 2,000 operating hours based on load and speed. High-grade grease or oil, engineered explicitly for bearing use, must be utilized as improper lubricants will damage performance. Of equal importance is the lubrication operating conditions. A bearing should generally operate at under 70 degrees C, or 158 degrees F, some high performance implements may exceed that temperature. Temperature differences could indicate a bearing failure, poor alignment, or wear and should be dealt with immediately if that happens.
Furthermore, visual observations should be conducted to detect signs of wear, corrosion, or contamination, which can worsen without attention. Monitor for any strange noises, such as grinding or rattling, as these could indicate possible issues that may arise. One practice that should be adopted is cleaning parts following to the bearings to avoid making the way for debris into the bearings. In addition, a detailed maintenance record should help monitor all the potential risk areas. Practicing such ideas would significantly enhance the operational life of the bearing in pumps and ensure that the entire system is in good working condition.
Warning Signs to Watch Out for and Help Reduce Repair Cost
Watching out for early signs of failure can save time in attending to repairs, cost in terms of money, and cost caused by the downtime of the equipment or machine. Some of the ‘red flags’ that can suffice to indicate a problem include shrill sounds emanating during operation, continuous vibration, or changes in the expected coolant temperature. For example, a bearing and or a component that is improperly aligned may lead to grinding or whining sounds, and excessive vibrations buying poorly balanced or loose parts may lead to adverse effects. A general rule of thumb says that maintaining vibration less than 4.5 mm/s RMS would help avoid stress on the parts of the machinery. Likewise, having working temperatures above 70°C would suggest there could be cases of overheating or a lubrication problem that needs urgent attention.
The problems and circumstances must be tackled early on to prevent any further damage, hence constant monitoring and repairing of the situation is a must. It is necessary to employ vibration measurement devices to monitor vibrations and spot minor alignment errors so they do not worsen. Thermal imaging may be essential for locating hot spots or measuring temperatures that present a threat of overheating. A scheduled routine can be set to check on lubrication, clean up, or visually check over significant components. Belts, seals, and fasteners should be visually monitored for wear out, as neglecting them will result in lousy machinery problems.
Addressing these signs as quickly as possible saves one from expensive repairs and helps keep the machinery in good condition for extended periods. Purchasing promising diagnostic tools and appropriately training personnel to detect possible warning indicators can help reduce risk while maintaining machinery functioning without disturbance.
Use the Correct Power Steering Fluid, as this Assures Durability
It is key to choose correctly the power steering fluid as this, in the end, determines the actual durability and functioning of the power steering system – remember that all power steering systems have been designed to work only with a particular formulation of fluid, so these provide the lubrication and pressure and wear protection needed. Utilizing fluids not recommended for that specific power steering system could raise problems like unwanted friction, overheating, and faster wear and tear of hoses and seals. Make sure you check the manual of your vehicle for the right fluid, there are manhy others who will have precise indications as to which mineral-based can be used, as well which systems would ideally require the synthetic fluid formulations.
There are also other essential factors to consider, like relative viscosity, boiling point, and degree of anti-foaming that the power steering fluid has. For example, in most power steering systems, while it may be custom to operate at ckt, it is suitable to have fluid viscosity stern differing of about ten cst -100. This allows for smoothing out the hydraulic and steering, as well as smoothing out movements and systems. Furthermore harnesses that resist oxidisation and corrosion should also be present, these would go a long way in improving the service life of the components as well. Unless provided otherwise in the approved consensus, do not mix fluids, as this will compromise the performance and fuel over time.
If possible, monitor fluid levels during periodic maintenance procedures to ensure the system remains efficient. The fluid should be clean and free of particles; water-logged or stained fluid usually requires a new power steering system. Depending on how you drive, the manual or the dealer suggests replacing the power steering fluid every 30,000 to 60,000 miles. If you carefully use the correct fluid and adhere to a regular maintenance pattern, you can extend your power steering system’s service life and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the procedure for replacing a power steering pump bearing step by step?
A: The process begins with removing the pump, replacing the old bearing or attachments that house the bearing with newer or rebuilt ones, and installing the pump back in its original place. The process requires close attention when the pulley is detached, ensuring that the new power steering pump sits firmly. All required sides are correctly positioned before the power steering fluid can be poured back into the desired reservoir.
Q: How did you disconnect the Honda power steering pump from the Honda power steering system?
A: The first step begins with the disconnection of the belt, which makes the pump operational. The next thing would be to unscrew the pump from the engine together with unscrewing the screws holding the belts, as well as disconnecting the hoses. If you plan to use this method, search for Honda power steering forums for this information.
Q: Is power steering pump bearing repair possible without displacing the entire pump?
A: The power steering pump can be disassembled with new kits to fix the inner medical components, including the bearings. This option is significantly less expensive than replacing the entire unit, especially if the pump is in appropriate condition.
Q: Which components do you require for the power steering pump bearing replacement?
A: Consider that, besides a fluid pump depot for the PS fluid refill, a puller for pulley removal, a wrench assembly for bolt removal, and a press (for the new bearing installation) might also be essential.
Q: How do I know it is time to replace the power steering pump bearing?
A: Common signs are the noise or squeal friction on the pump, the feel of a steering problem, or a light indicator sign on the dashboard. If that is the case, it might be time to diagnose the bearing.
Q: Where can I purchase the power steering pump rebuild kit I am looking for?
A: Rebuild kits are usually available from auto part suppliers, online markets, or platforms where car owners and enthusiasts discuss their power steering. For effective results, remember to use the specifics of the desired kit’s car make and model.
Q: Should I top up the power steering fluid level after the bearing has been replaced?
A: After the bearing is replaced and the pump is reinstalled, you must add fluid to the power steering pump fluid reservoir. Also, make sure to check for leaks before the engine starts.
Q: What should I do if I can’t locate a suitable power steering pump for my car?
A: In case you cannot get a suitable pump, perhaps you can visit some online forums or check with the community dedicated sources that would suggest where to procure the parts. You may also consider a core charge option, which entitles you to send back your old one and get a new pump at a considerably cheaper price.







